Final Projects
yyds

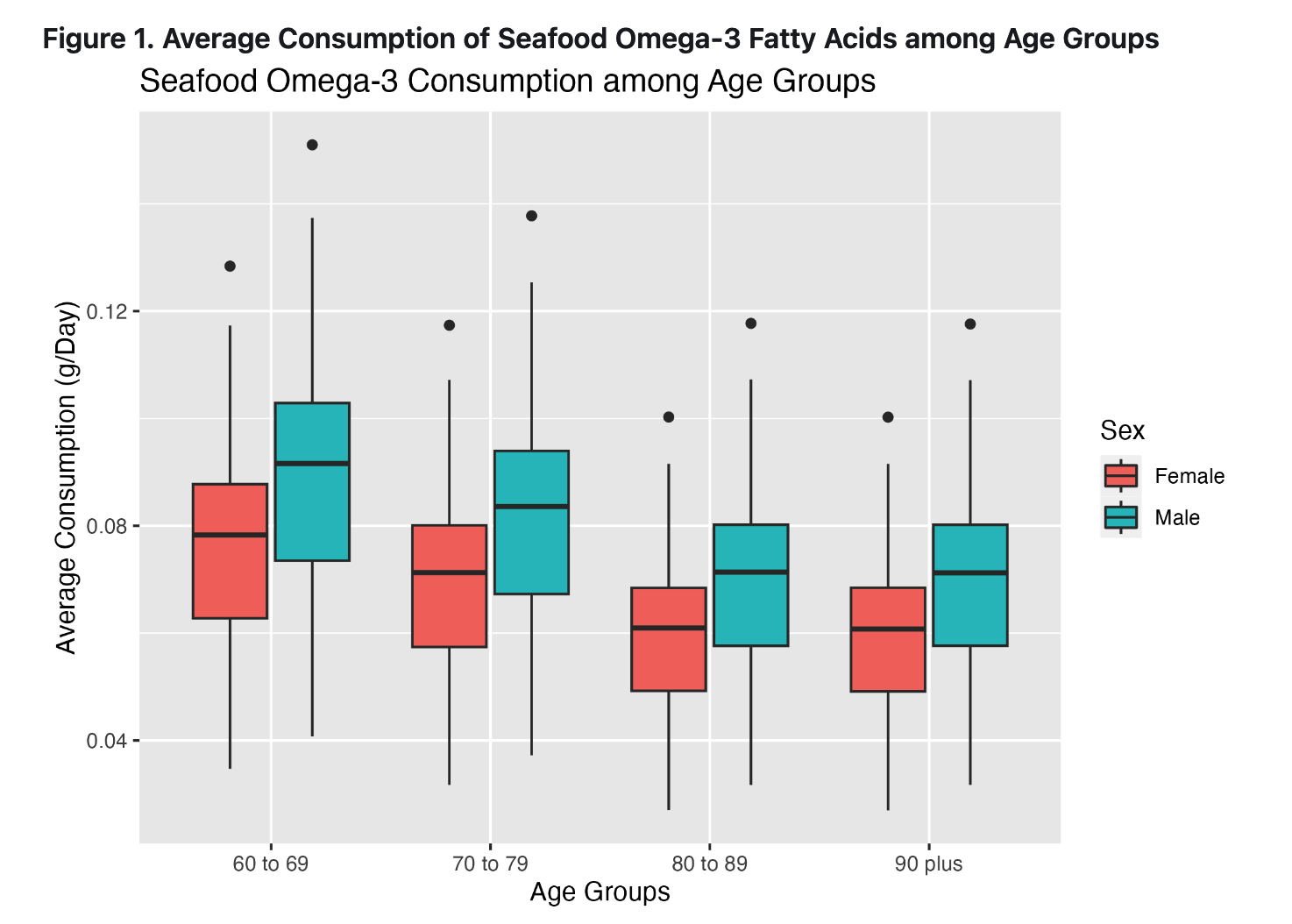
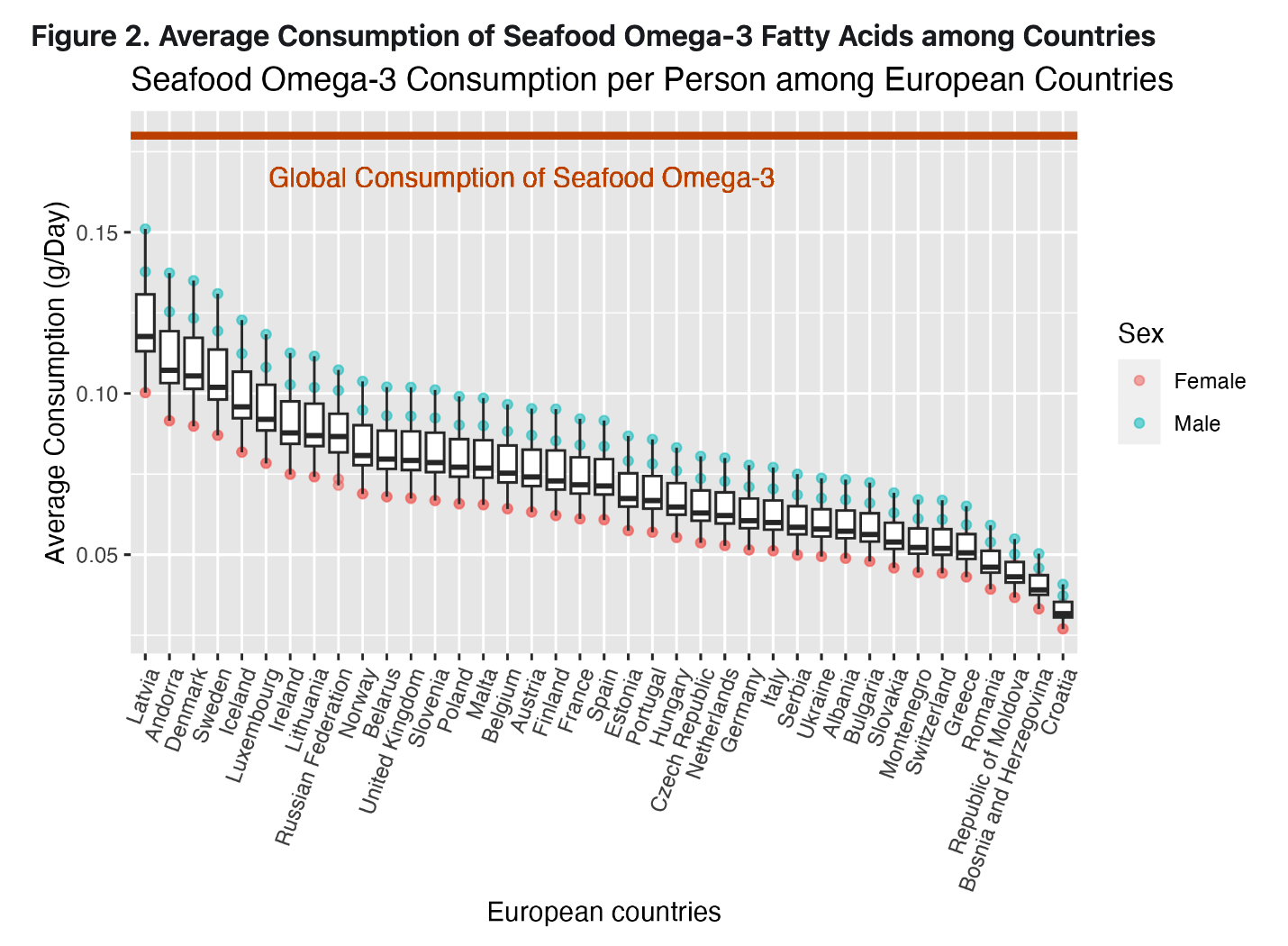
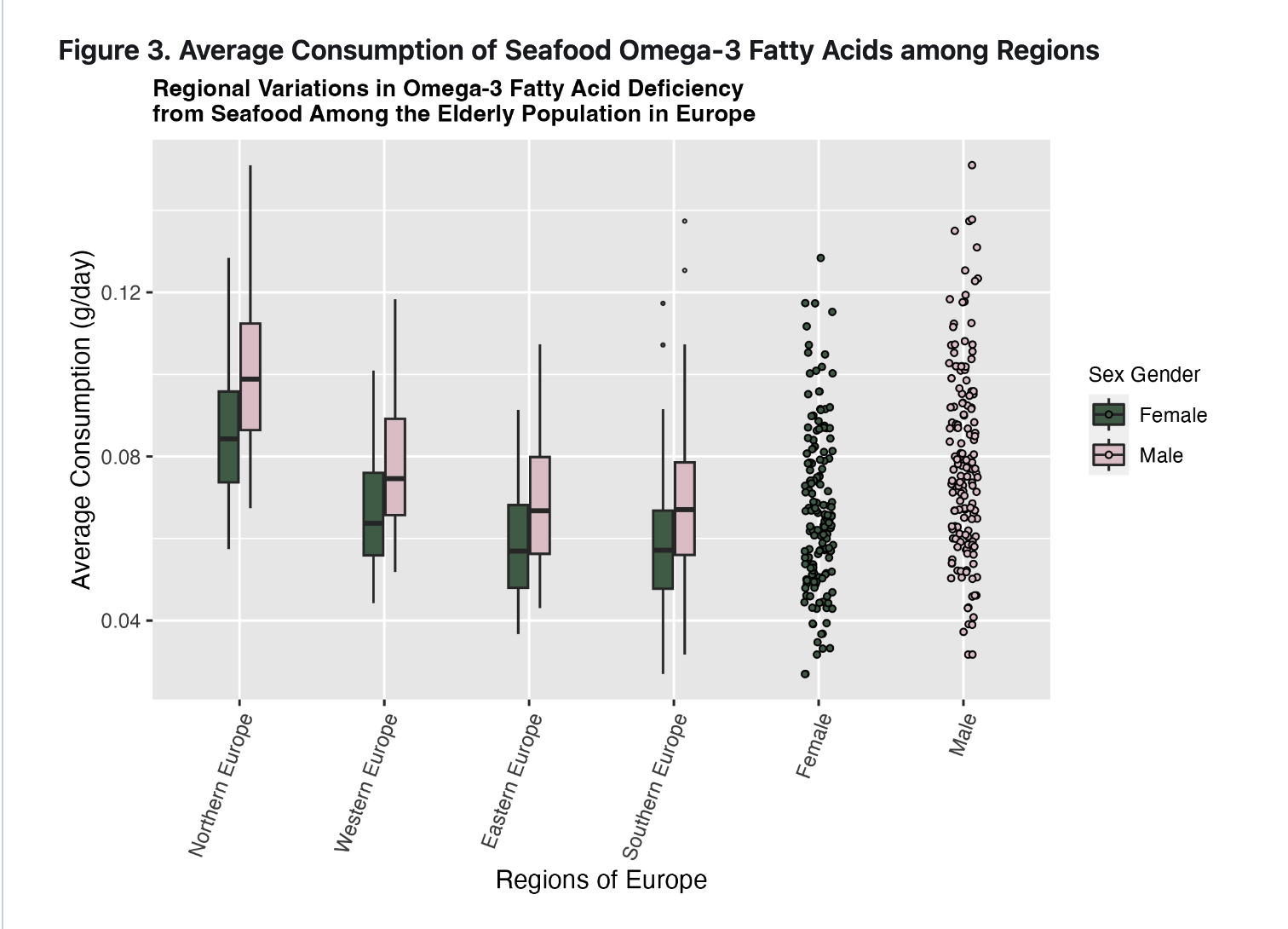
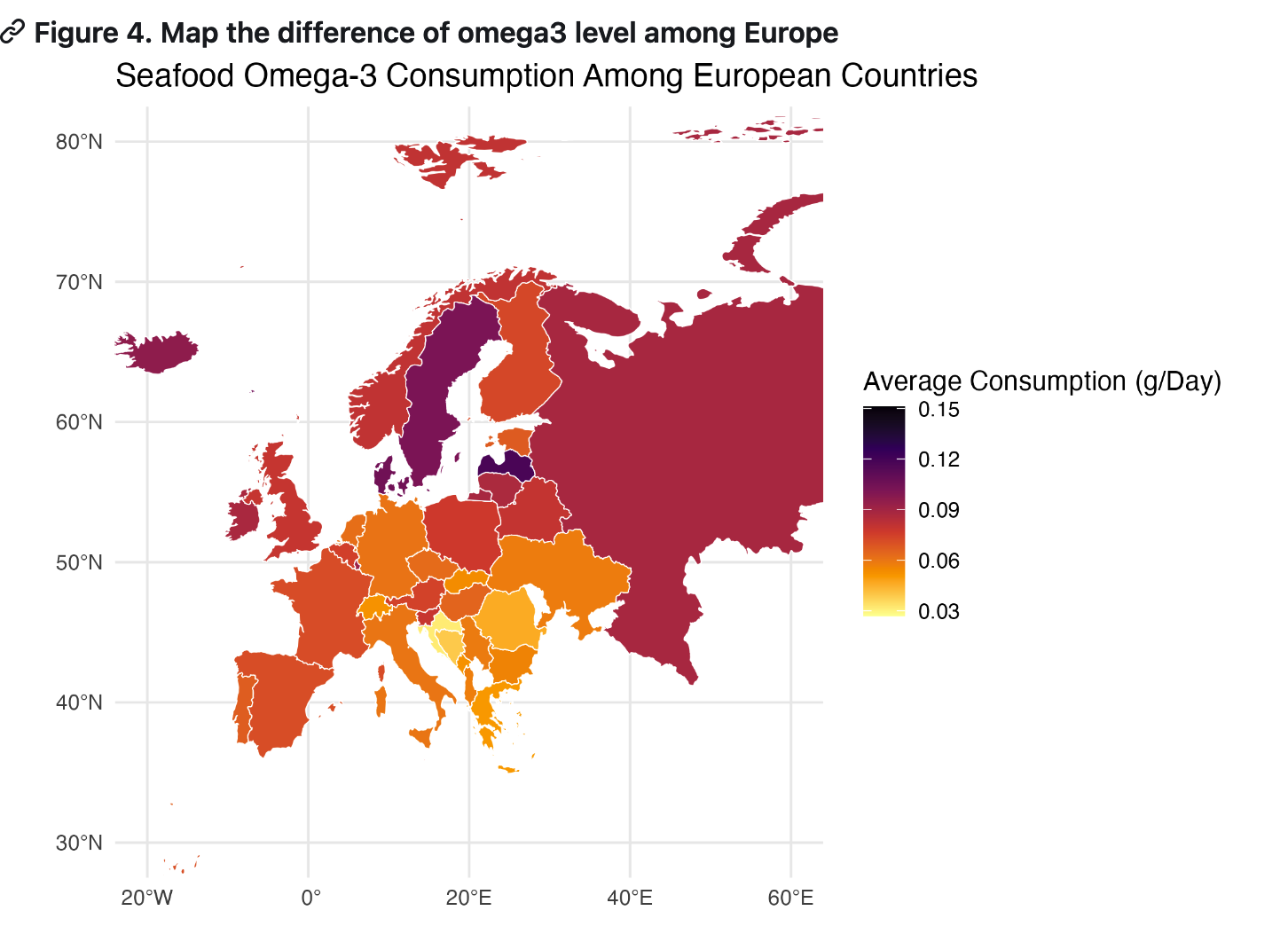
we R wizards




VADA-R
“We are team VADA-R, not to be confused with the “Darth” version from Star Wars.”
Introduction
For this project, we used the CDC’s Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity Data available at: www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpao/data-trends-maps/index.html
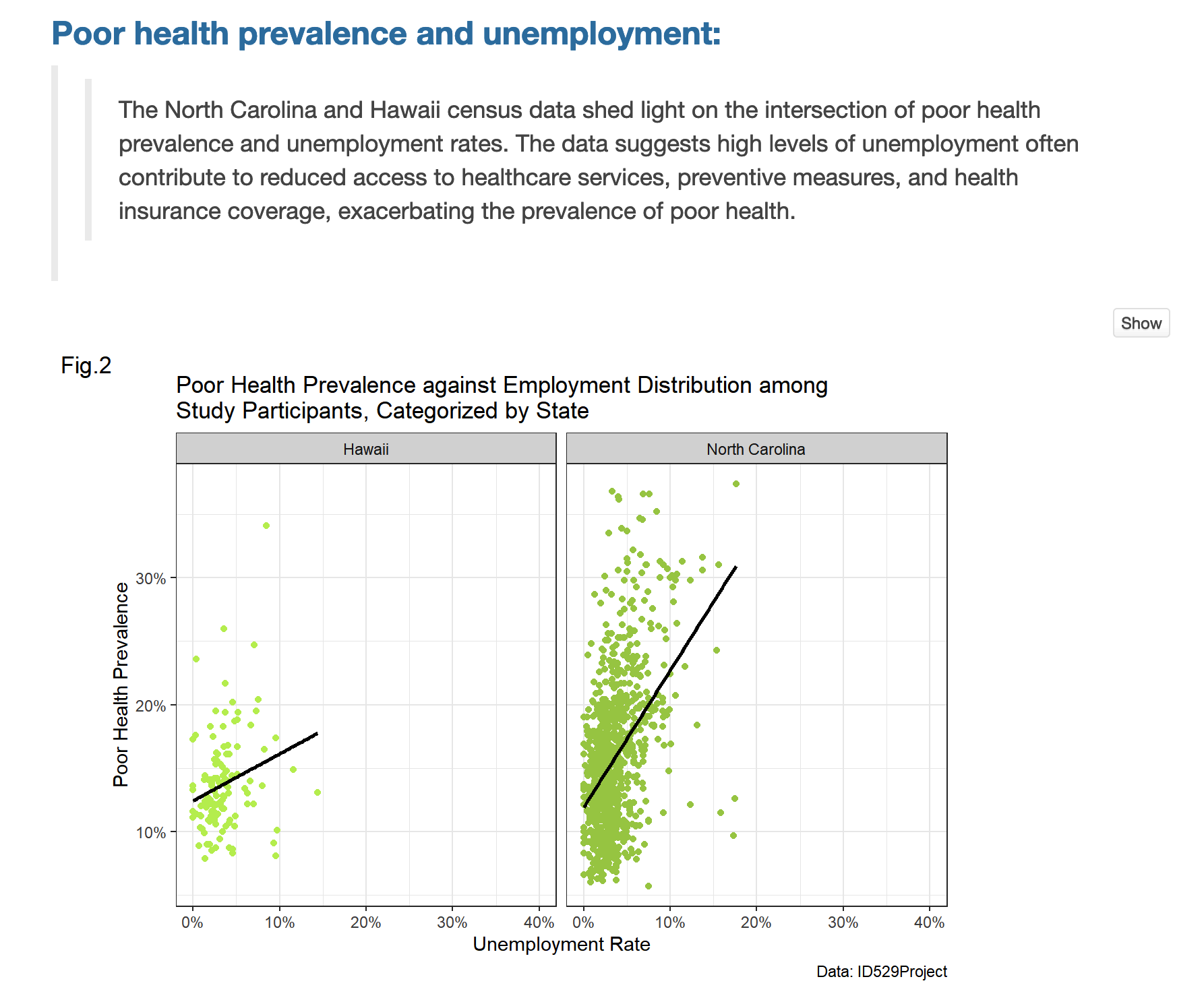
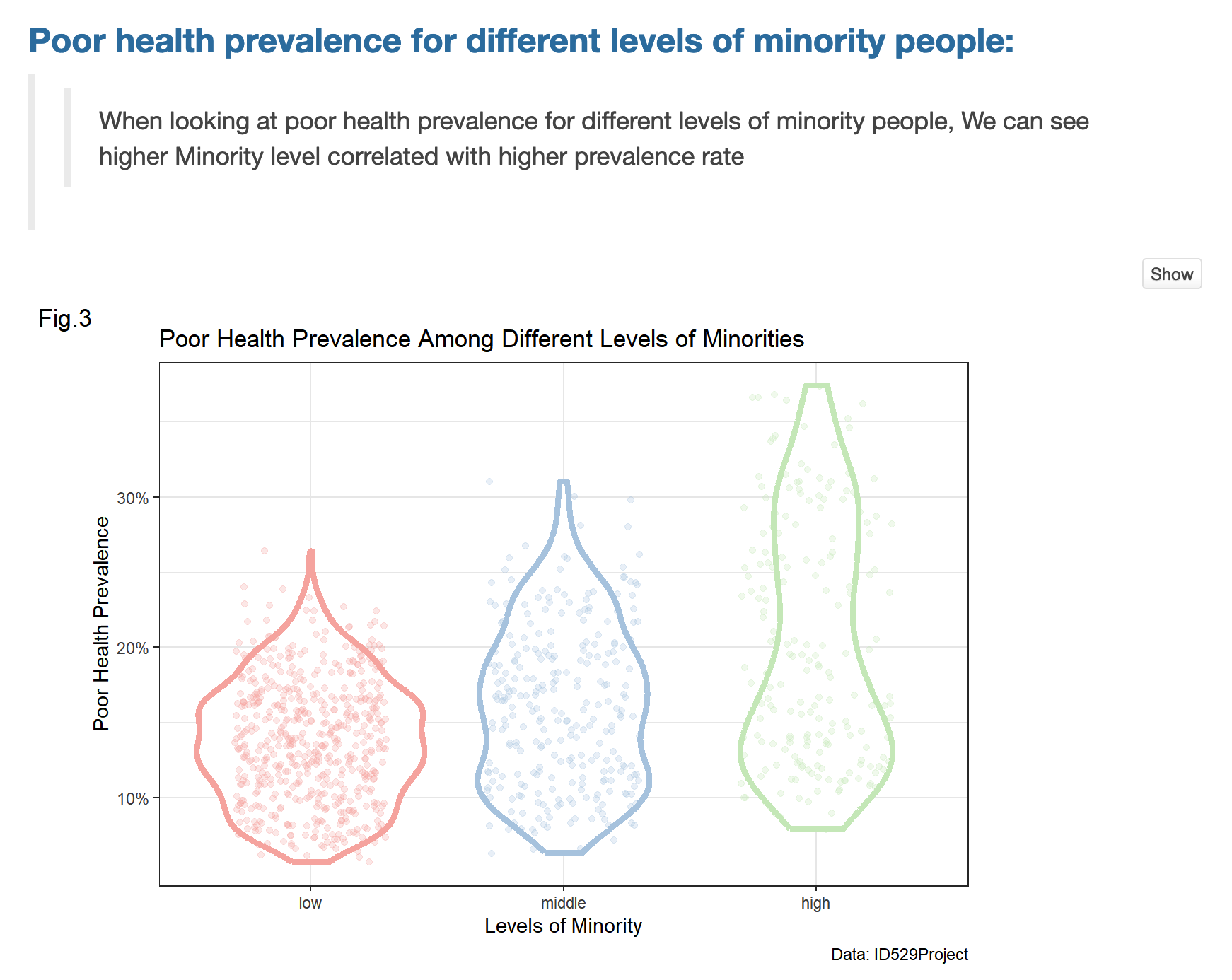
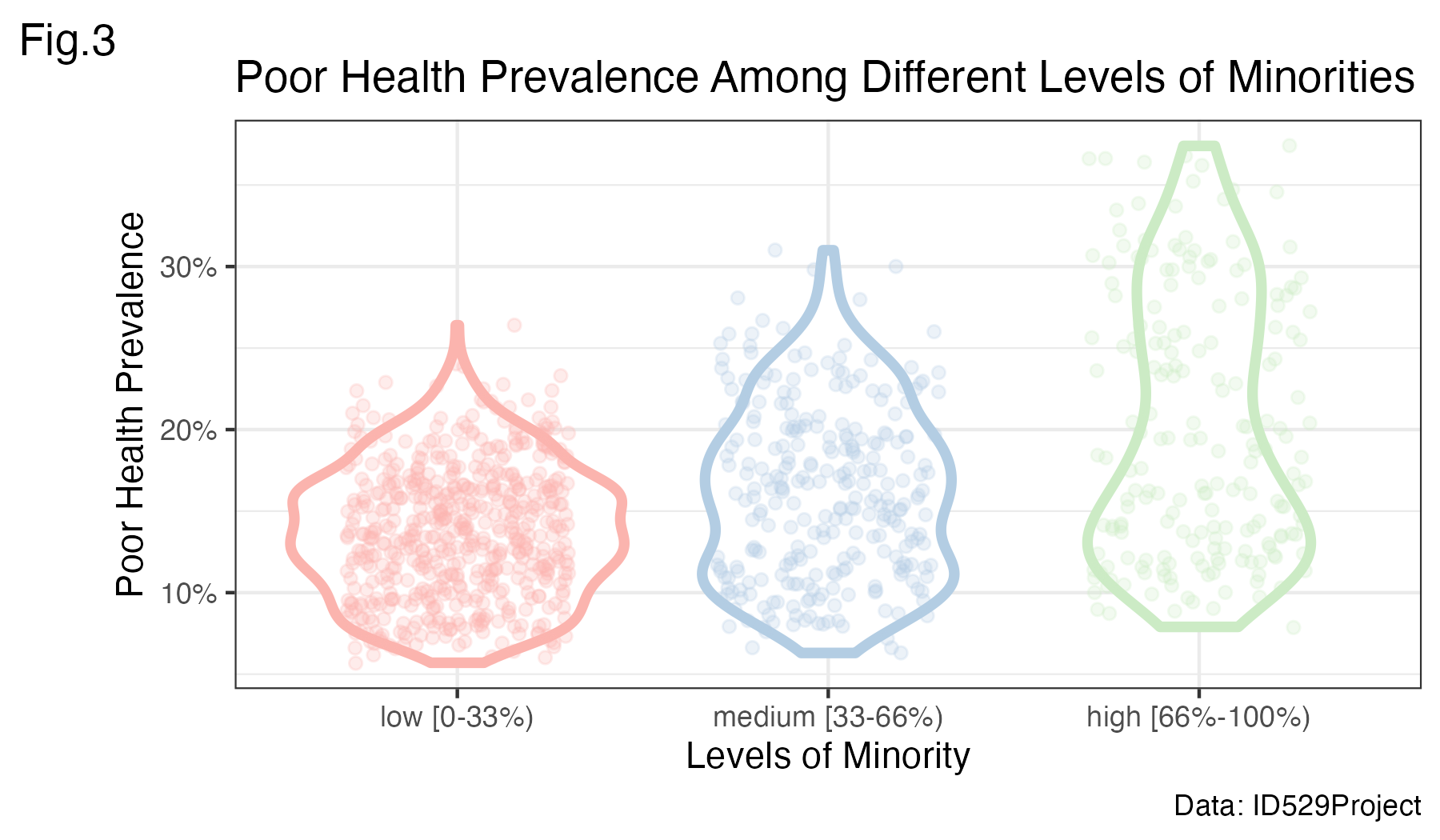
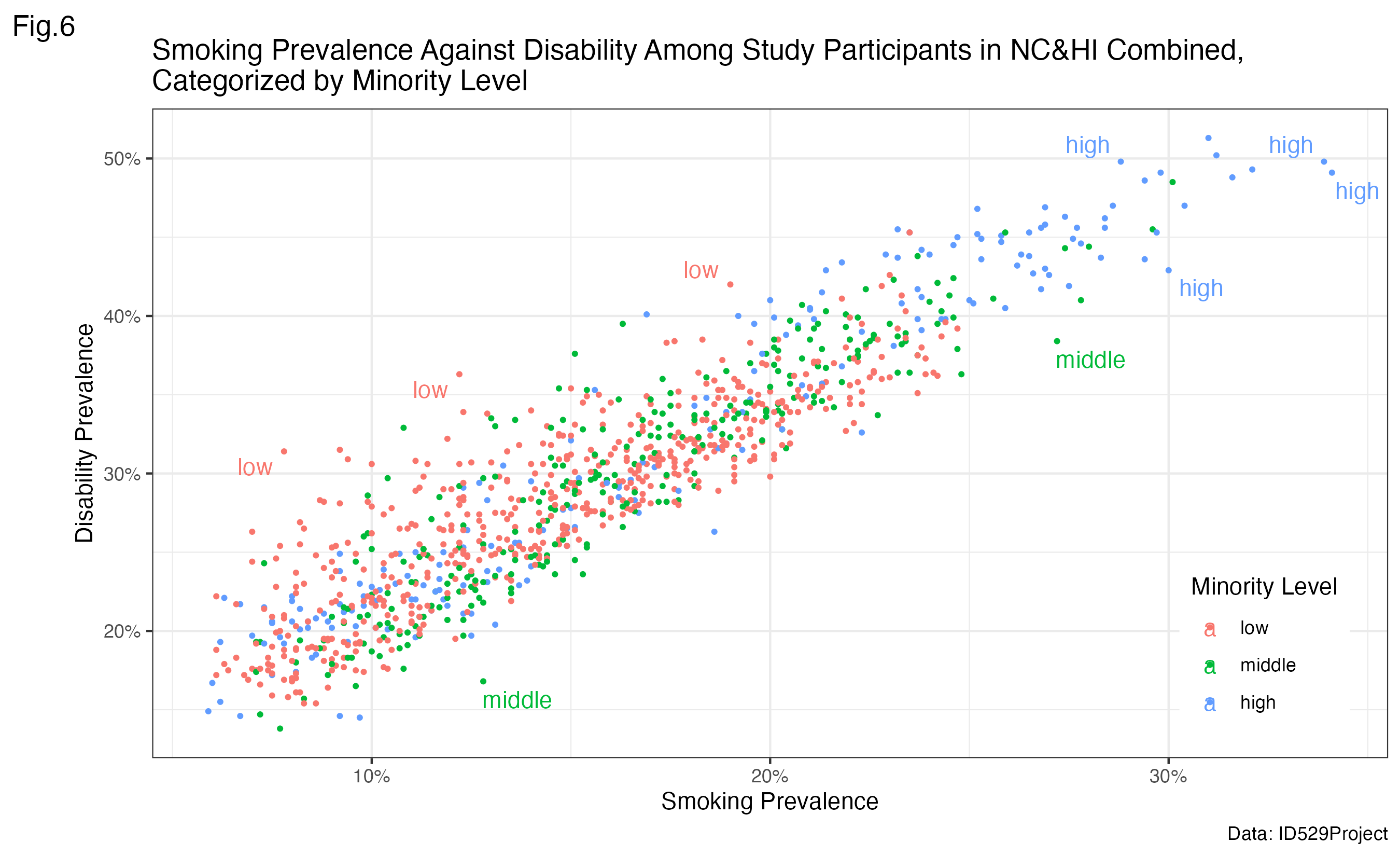
Motivation
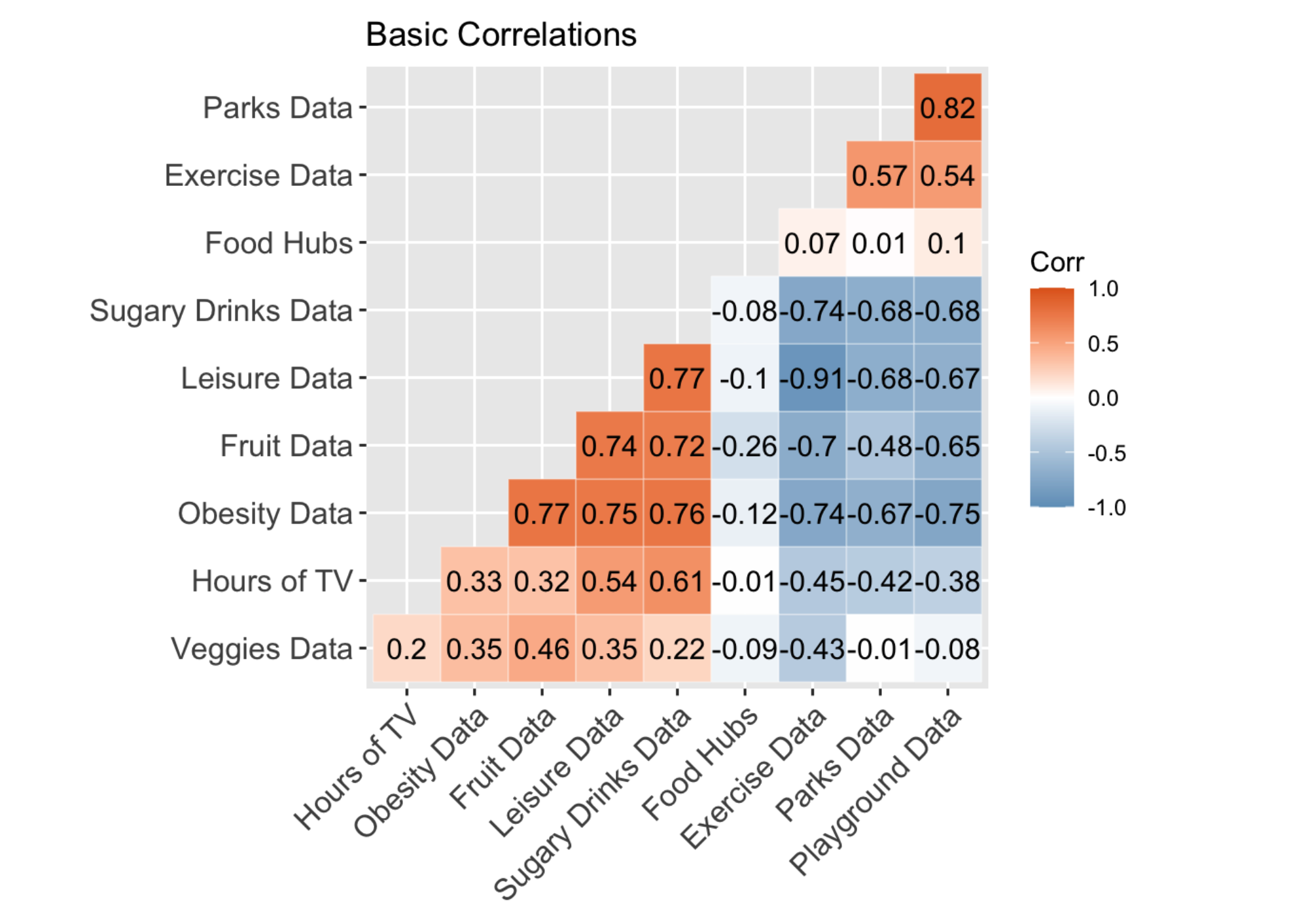
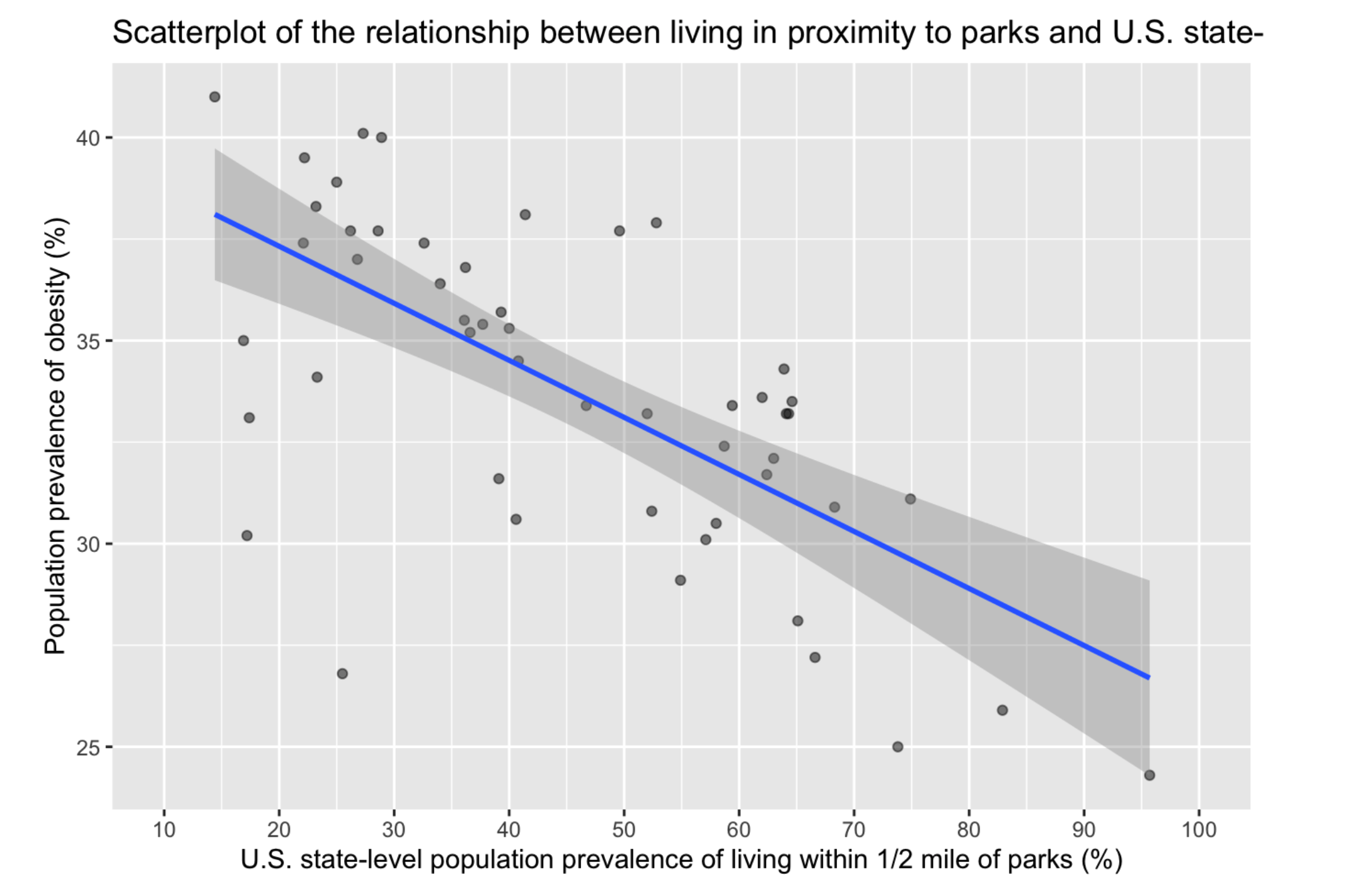
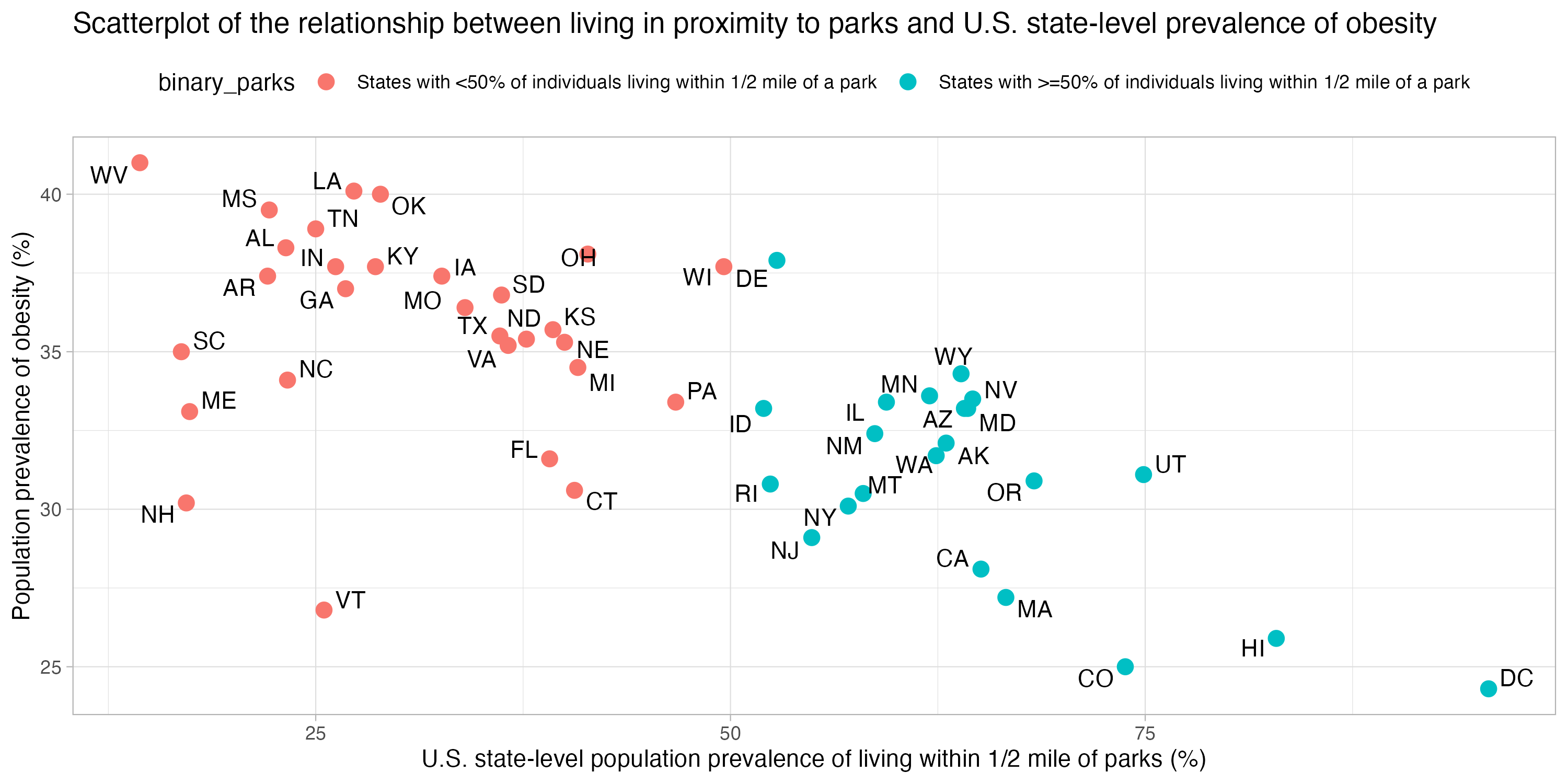
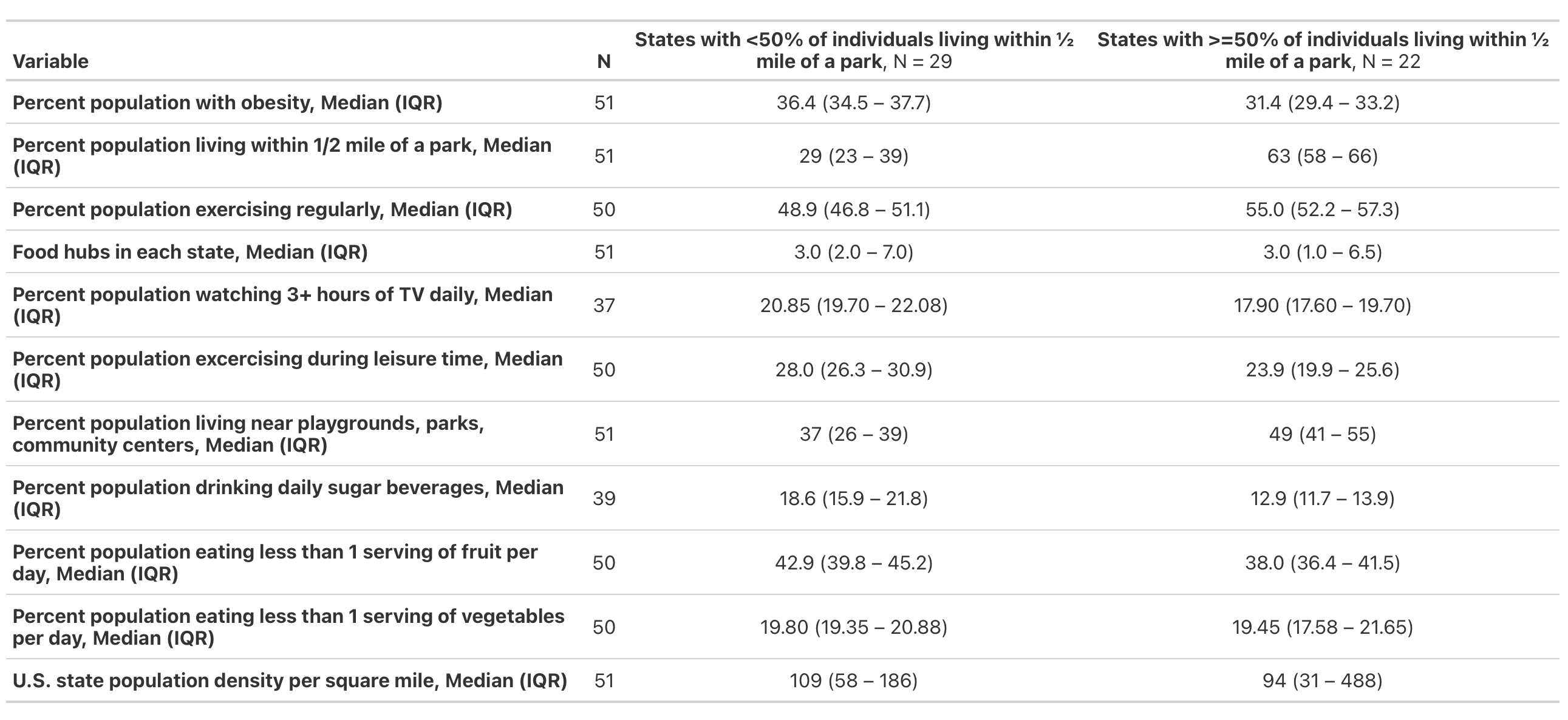
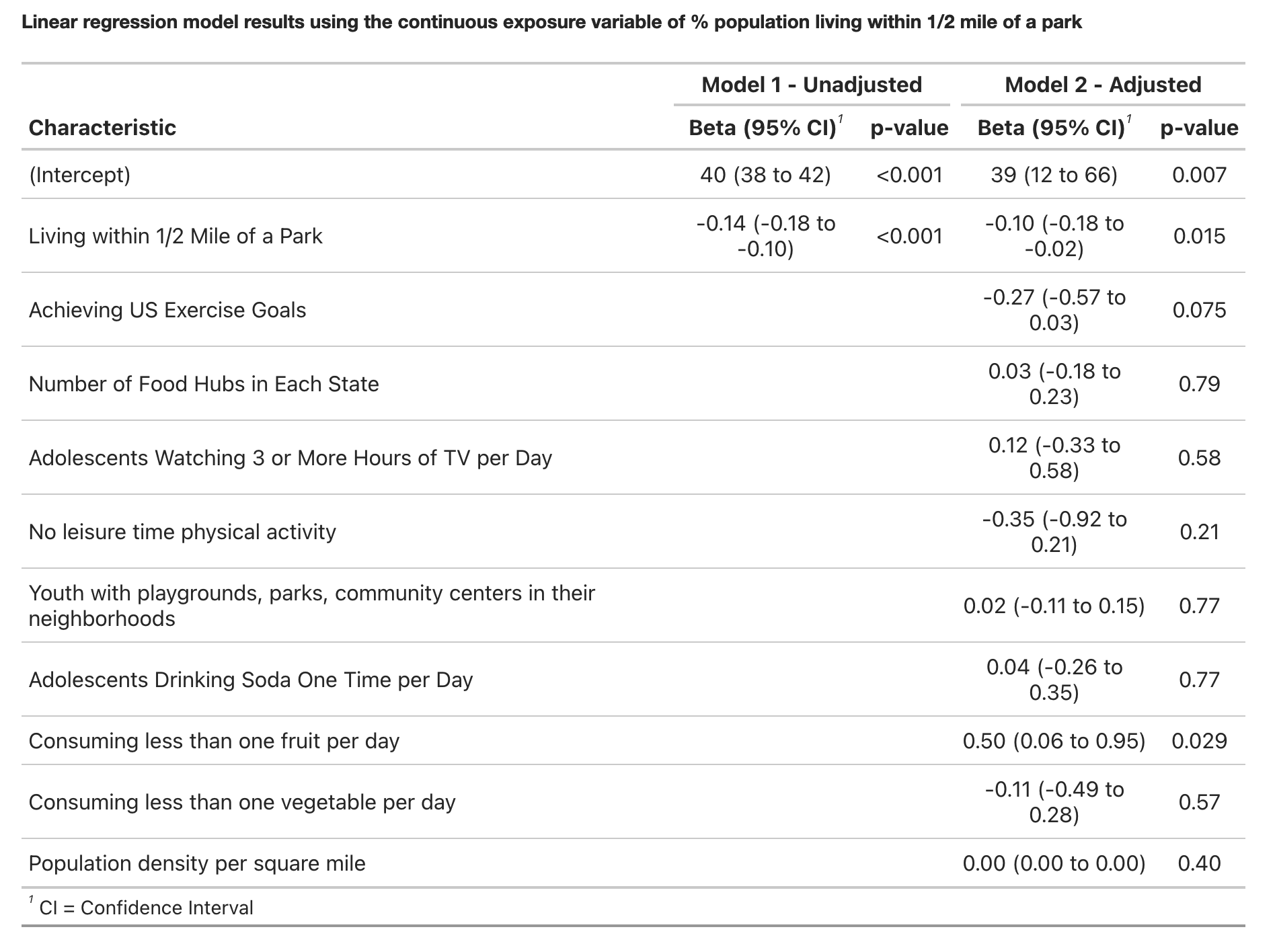
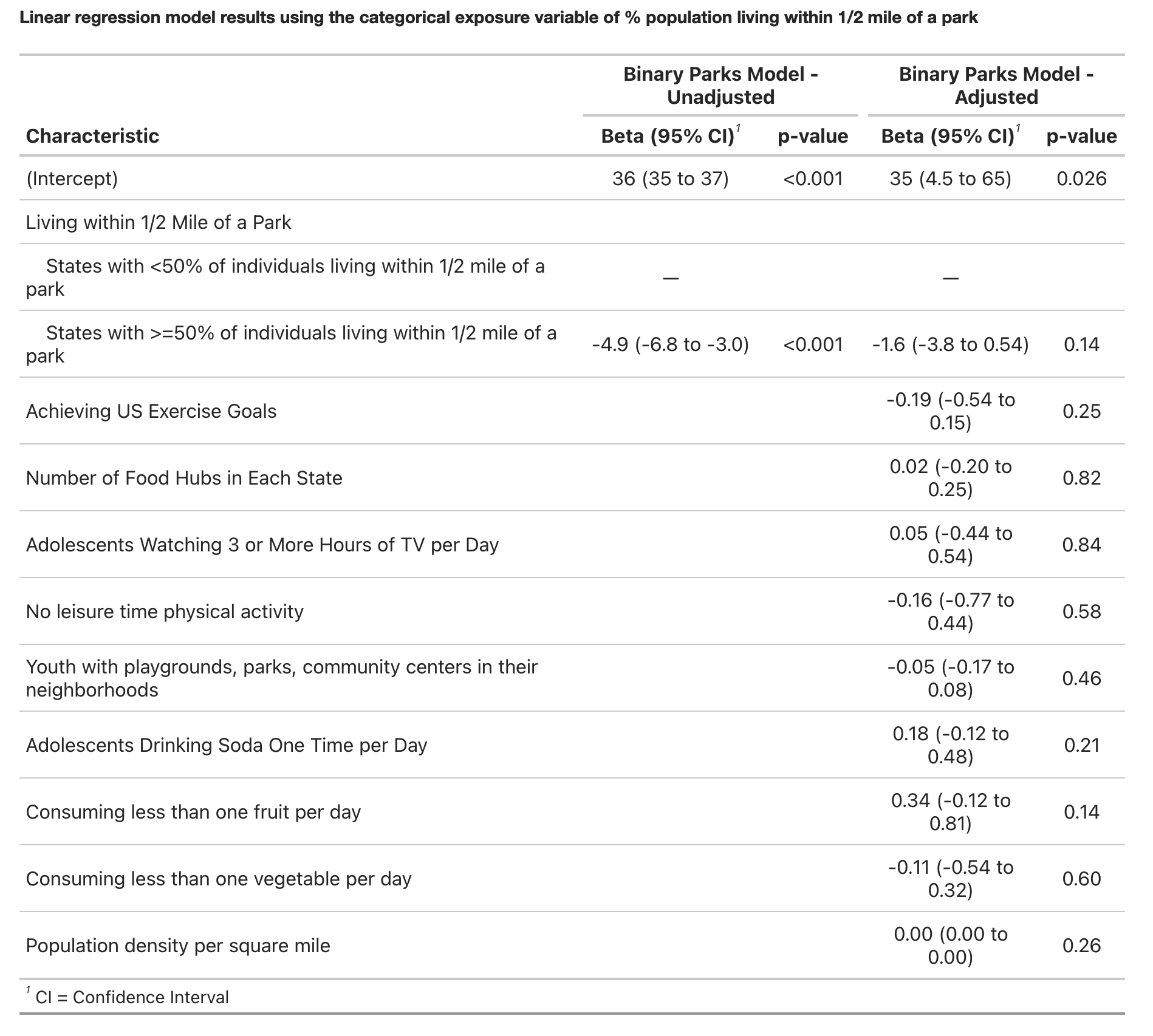
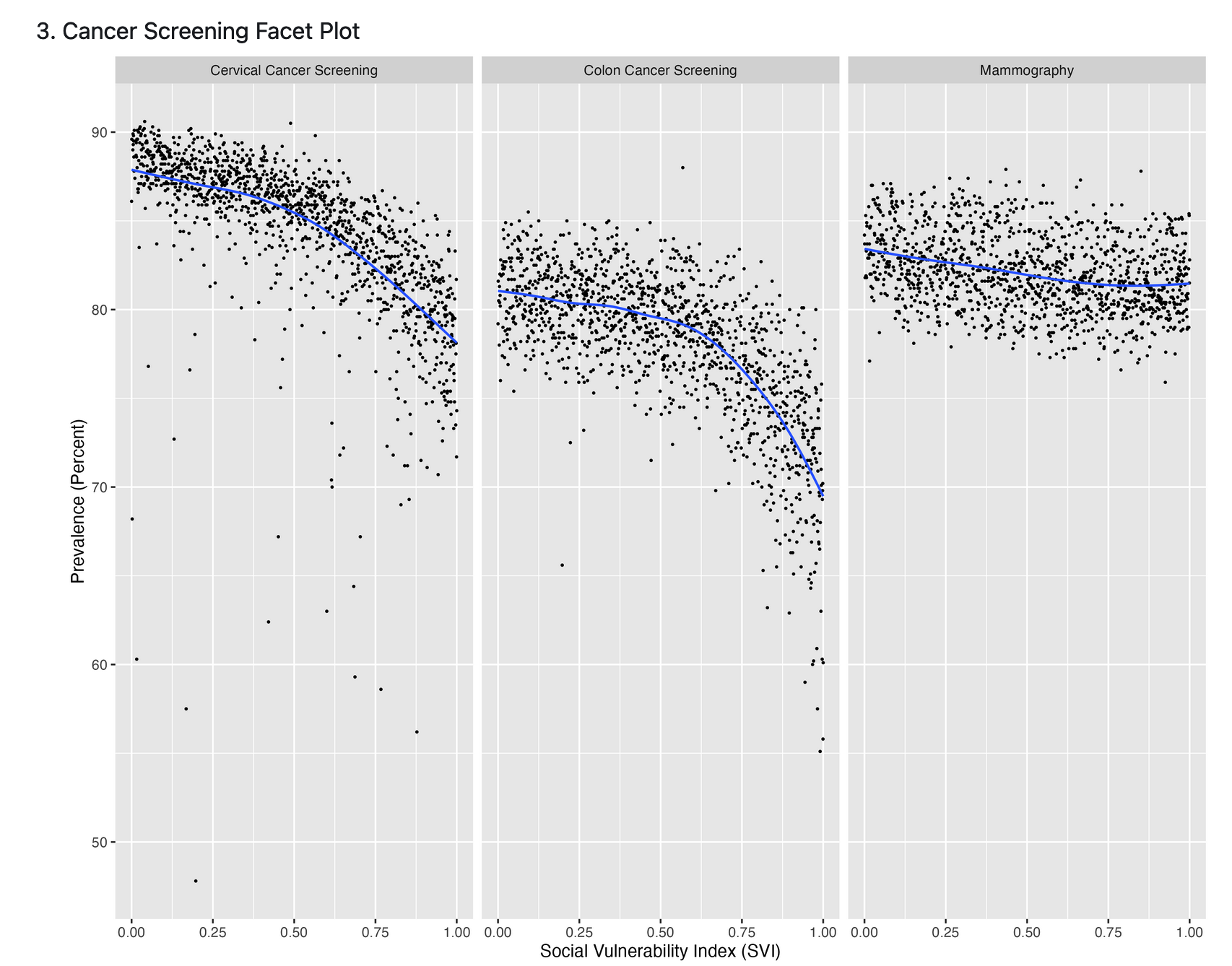
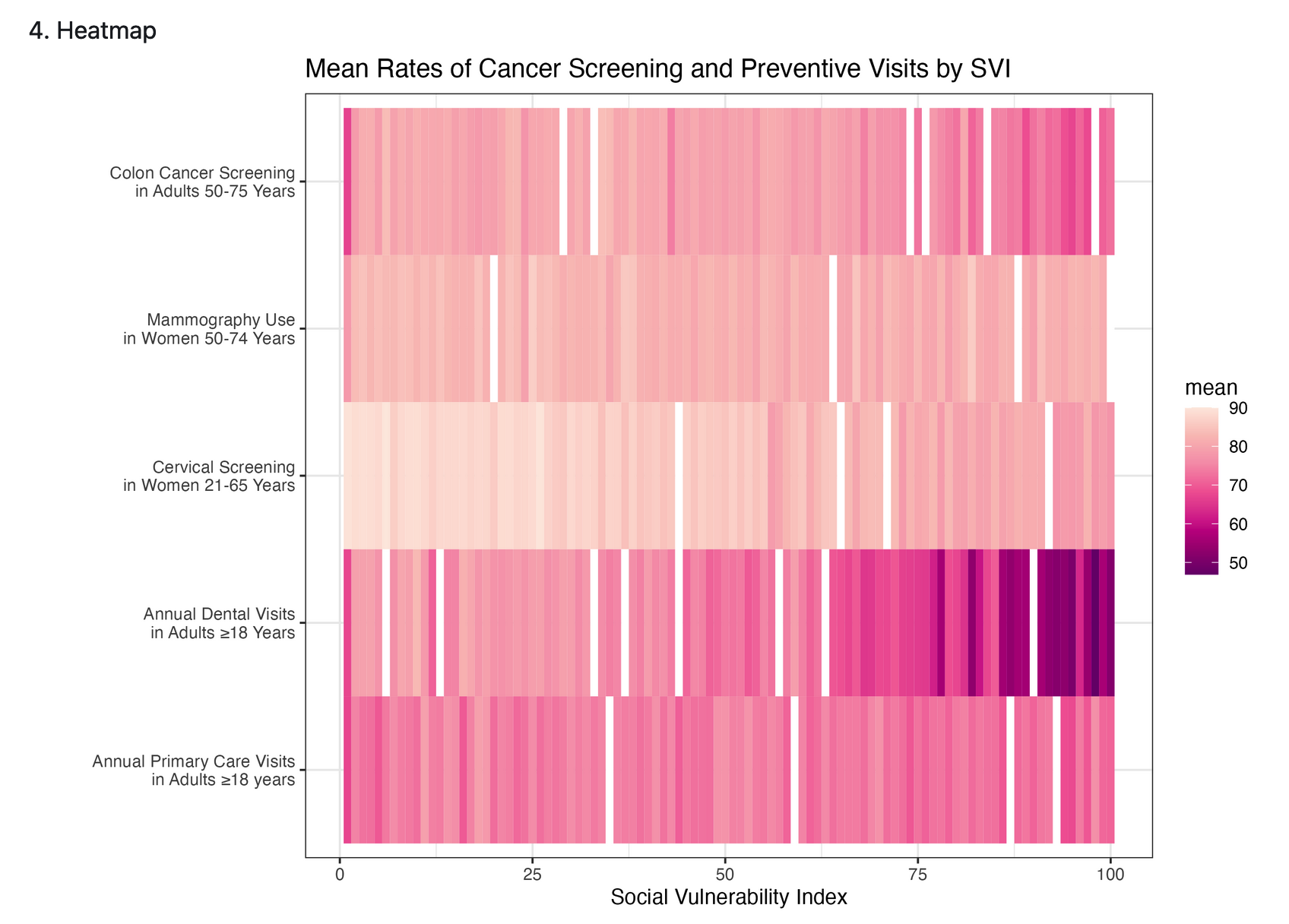
Our goal was to study the association of living near parks and population-level obesity in the US. Being inactive and leading a sedentary lifestyle are modifiable factors that are known to be associated with obesity. Accordingly, living near parks and other open spaces may encourage physical activity. However, whether living within close proximity to parks is associated with a lower population-level prevalence of obesity is unknown.
Hypothesis:
Using ecologic U.S. data, we hypothesized that populations living within close proximity to parks would have a lower prevalence of obesity.



R-made-simple



pediatrics-ED-nutrition



98_git_access.R

noel-fan-club

Introduction
Our study aims to determine the role of physical exercise as a therapeutic strategy for individuals with AD. This data analysis delves into the relationship between exercises and their potential impact on cognitive function, specifically focusing on improving the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores. MMSE is a widely used screening tool for cognitive impairment and dementia; consisting of a brief structured questionnaire that assesses various cognitive functions, including orientation, memory, attention, language, and visual-spatial skills. AD is characterized by progressive cognitive decline, which poses a significant challenge to individuals and society at large. We aim to investigate the potential benefits of exercise in mitigating cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s. By exploring the association between exercise and enhancements in MMSE scores, our study seeks to contribute valuable insights into how a physically active lifestyle may serve as a modifiable factor influencing cognitive well-being in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Information on dataset & variables
https://dataverse.harvard.edu/file.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/ER8ICT/A6HAVX&version=1.0 Summary of the Alzheimer’s Disease Exercise Program Trial (ADEPT: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01128361):
Study Design:
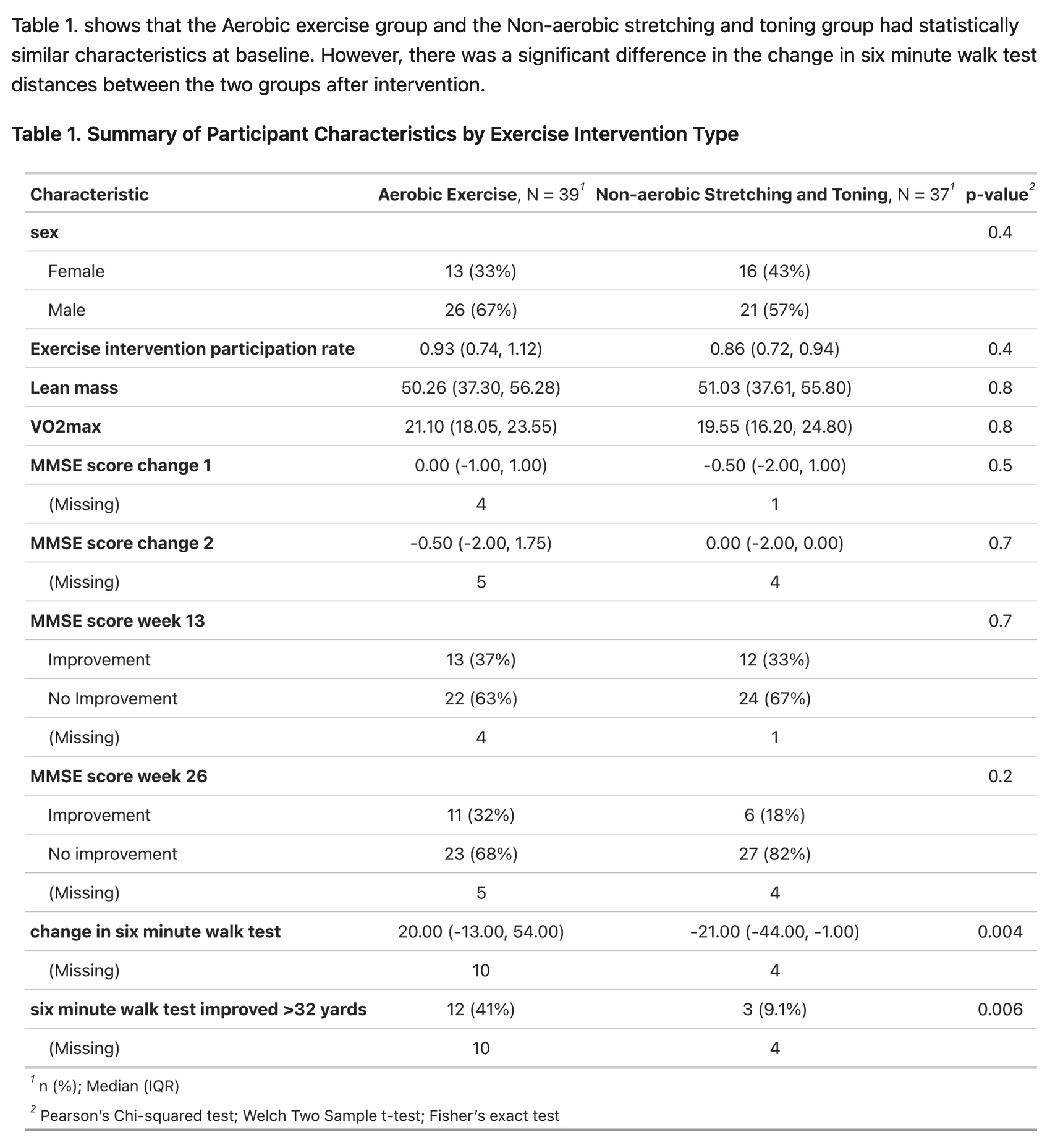
A pilot randomized controlled trial of 26 weeks of aerobic exercise (AEx) versus a non-aerobic stretching and toning control (ST).
Participant Information:
Included adults over 55 in the earliest stages of AD-related cognitive decline. Participants were assigned to AEx and ST groups in a 1:1 ratio. Recruitment from August 2, 2010 through September 26, 2014. Follow-up testing was completed by April 17, 2015.
Among 76 participants randomized into two groups, a total of 68 participants (89%: ST n = 34, AEx n = 34) completed the study.
Interventions:
AEx group
Began the intervention with a goal of 60min/week in Week 1 and increased weekly exercise duration by approximately 21min/week until they achieved the current recommended target duration of 150min per week, distributed over 3–5 sessions. Target heart rate (HR) zones were gradually increased from 40–55% to 60–75% of HR reserve based on resting and peak HR during cardiorespiratory fitness testing.
ST group
Performed a series of non-aerobic exercises that rotated weekly (core strengthening, resistance bands, modified tai chi, modified yoga). Participants wore HR monitors and were asked to keep their HR < 100 bpm. Exercise trainers helped participants adjust exercise intensity to reduce HR as necessary.
Both groups were supervised by exercise trainers during weeks 1-6 and gradually reduced supervised sessions to 1 per week based on perceived ability to be safe and independent and in consultation with the participant’s study partner and study staff.
Variables Description
Independent Variables - DurationPct : Percentage of prescribed exercise completed by participant.
Dependent Variables - MMSE : Mini-mental State Exam; The MMSE is a paper-based test with a maximum score of 30, with lower scores indicating more severe cognitive problems. The cut point established for the MMSE defines ‘normal’ cognitive function and is usually set at 24, although theoretically it could fall anywhere from 1 to 30. Will be making two new variables: (1) week 13 – baseline, (2) week 26 – baseline.
Covariates - Age : Age in years
- Sex : Sex (female, male)
- Edu : Education in years
- Lean_Mass : Lean body mass in kg
- Max_VO2_mL : Maximal oxygen consumption during a graded exercise test in mL/kg body mass/minute - Six_Min_Walk : Six-minute Walk Test in yards –> converted to meters and into binary variable (with cut-point difference >=32, <32)
Others - IDn : Participant ID Number
- Timepoint : Timepoint of Measurement; baseline/week13/week26
- Arm : Intervention Arm; ST/AEx
statistical analysis
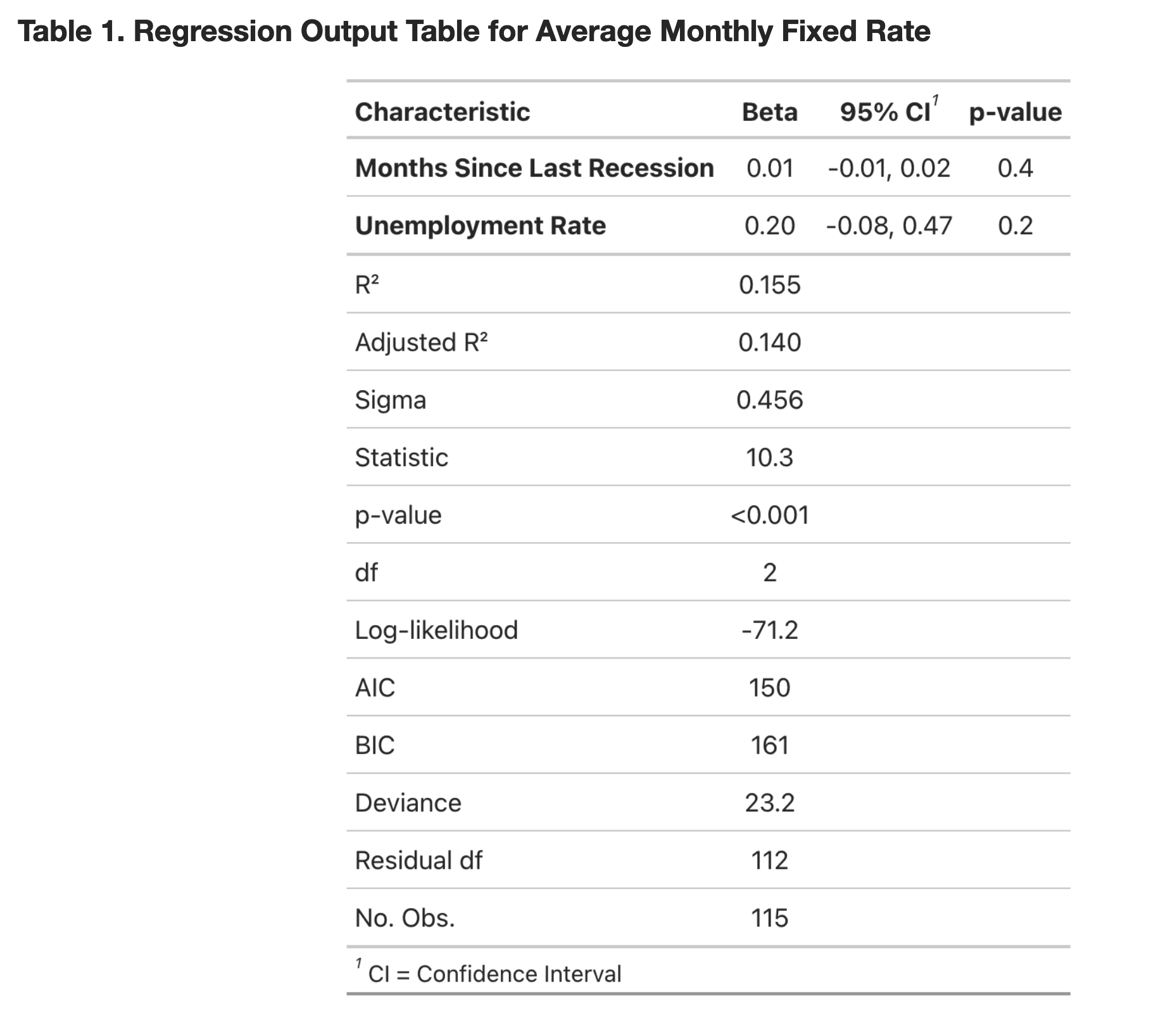
A linear regression analysis of the effect of treatment arm on our primary outcomes using R
Participants were included in analyses regardless of protocol adherence (As-treated analysis)
- Outcome: Change in MMSE score
As Continuous variables - Outcome 1: week 13 - baseline
- Outcome 2: week 26 - baseline
As Categorical variables - MMSE score week 13: Improved, Not improved - MMSE score week 26: Improved, Not improved - Fixed effects: Treatment Arm (AEx, ST)
- Models
- Model 1: Outcome (Δ MMSE) ~ Treatment (Duraction Pct) + Fixed effect (treatment arm)
- Model 2 (sociodemographic variables adjusted): MSSE ~ Model 1+ Age, Sex, Edu
- Model 3 (lifestyle variables included): MMSE ~ Model 2 + Max_VO2_mL, Six_Min_Walk, Lean_Mass - Model 4 (sensitivity analysis; exclude lean mass): MMSE ~ Model 2 + Max_VO2_mL, Six_Min_Walk,
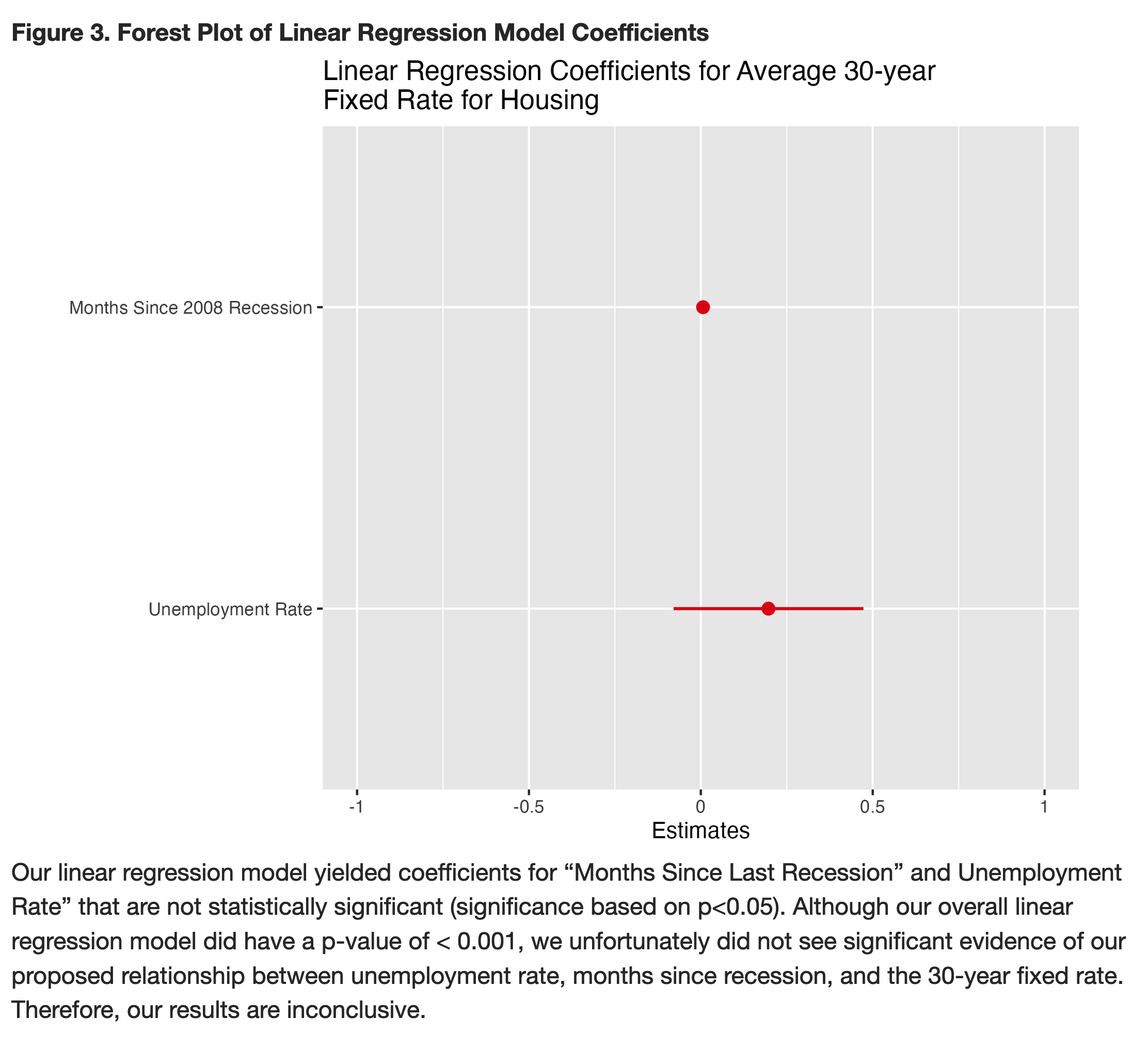
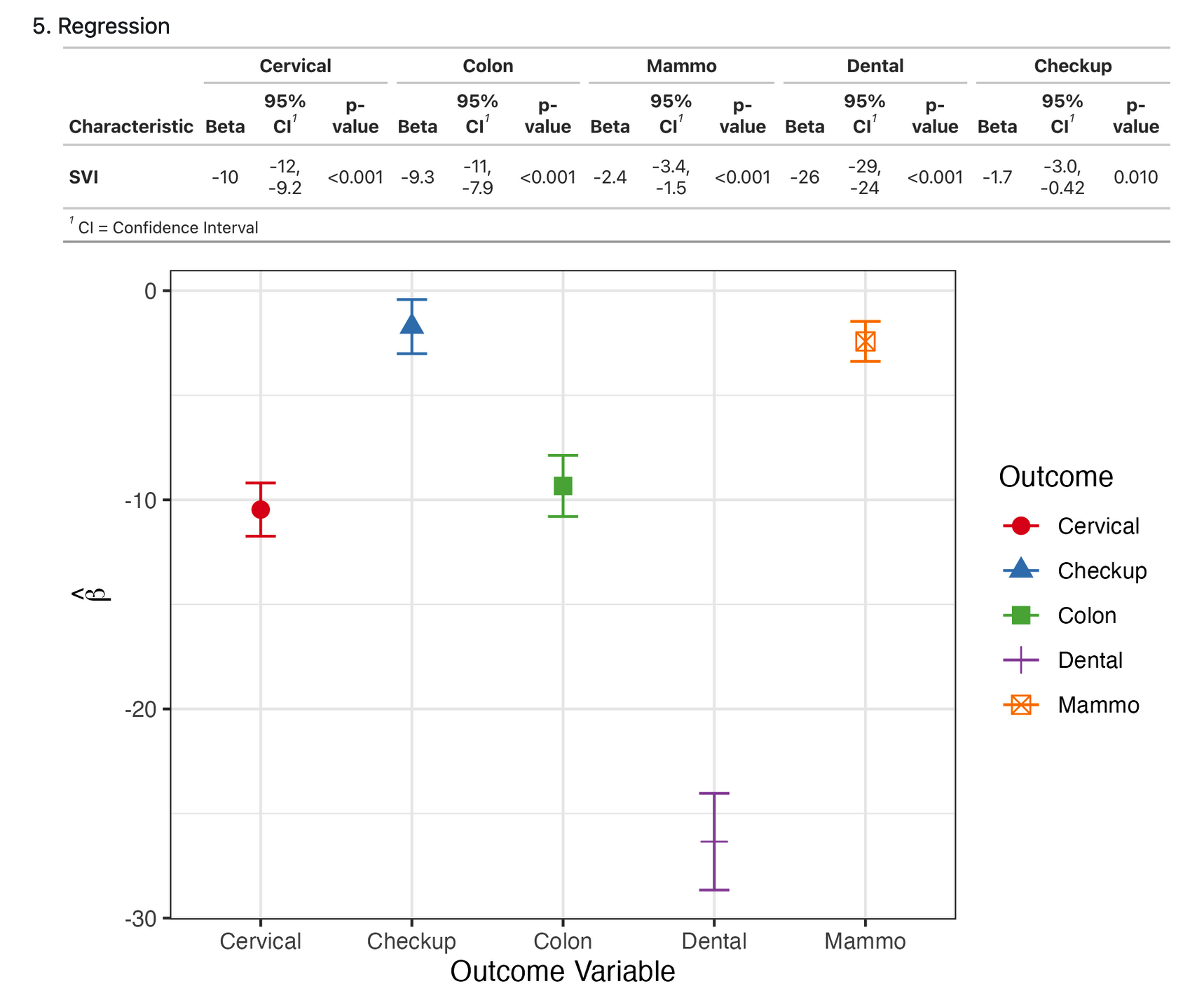
The covariates and confidence intervals will be obtained and visualized by forest plots
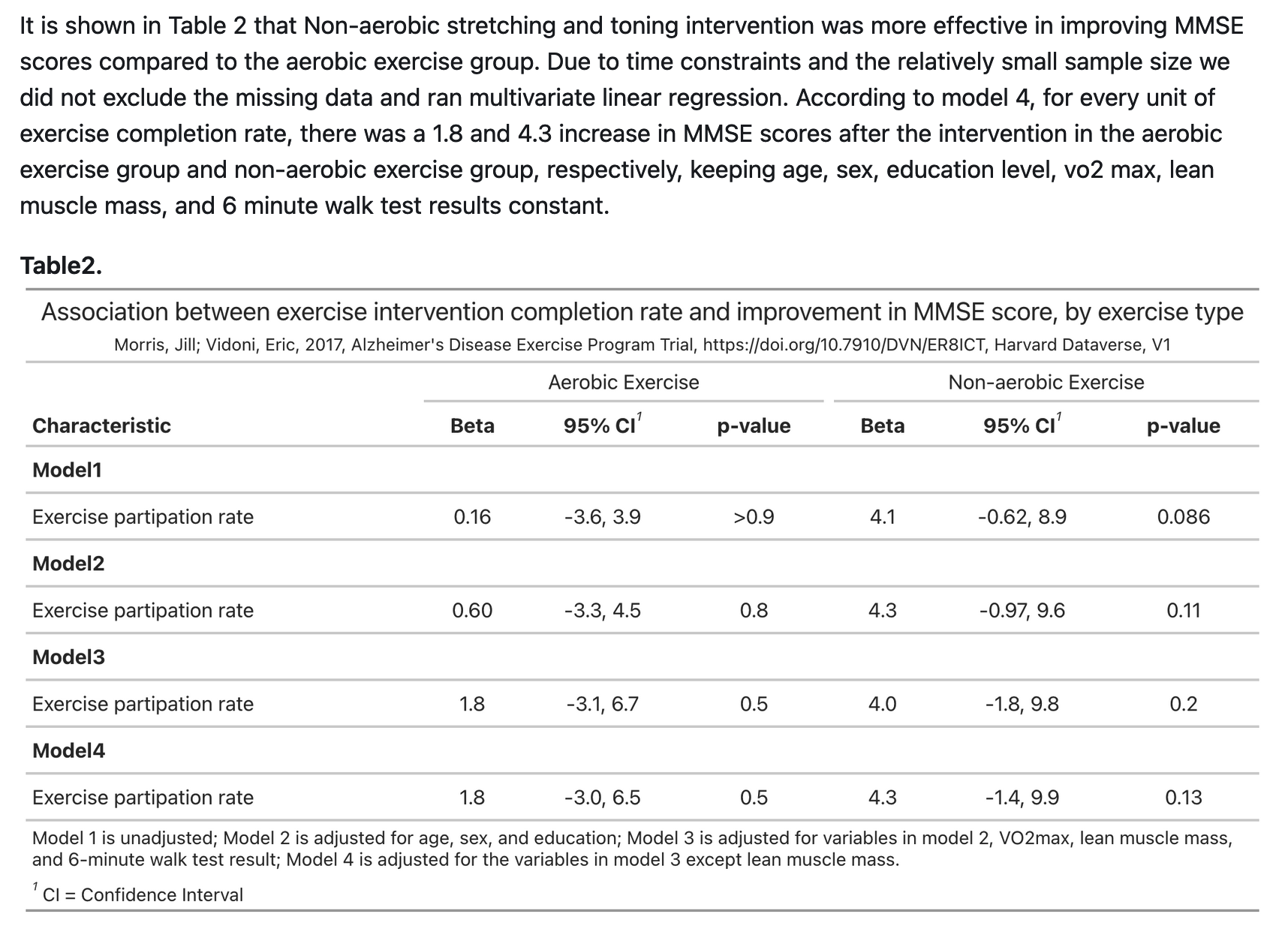
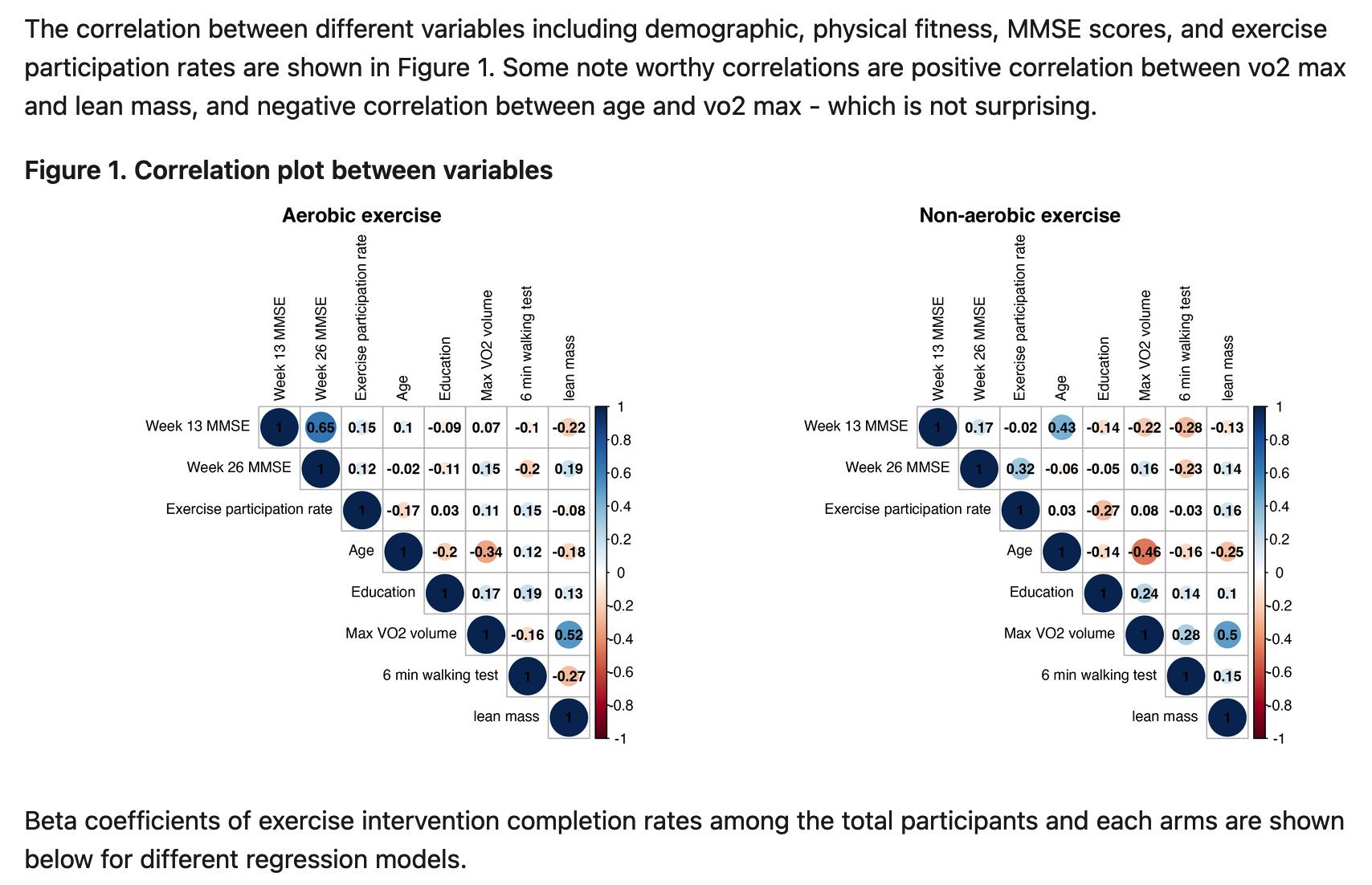
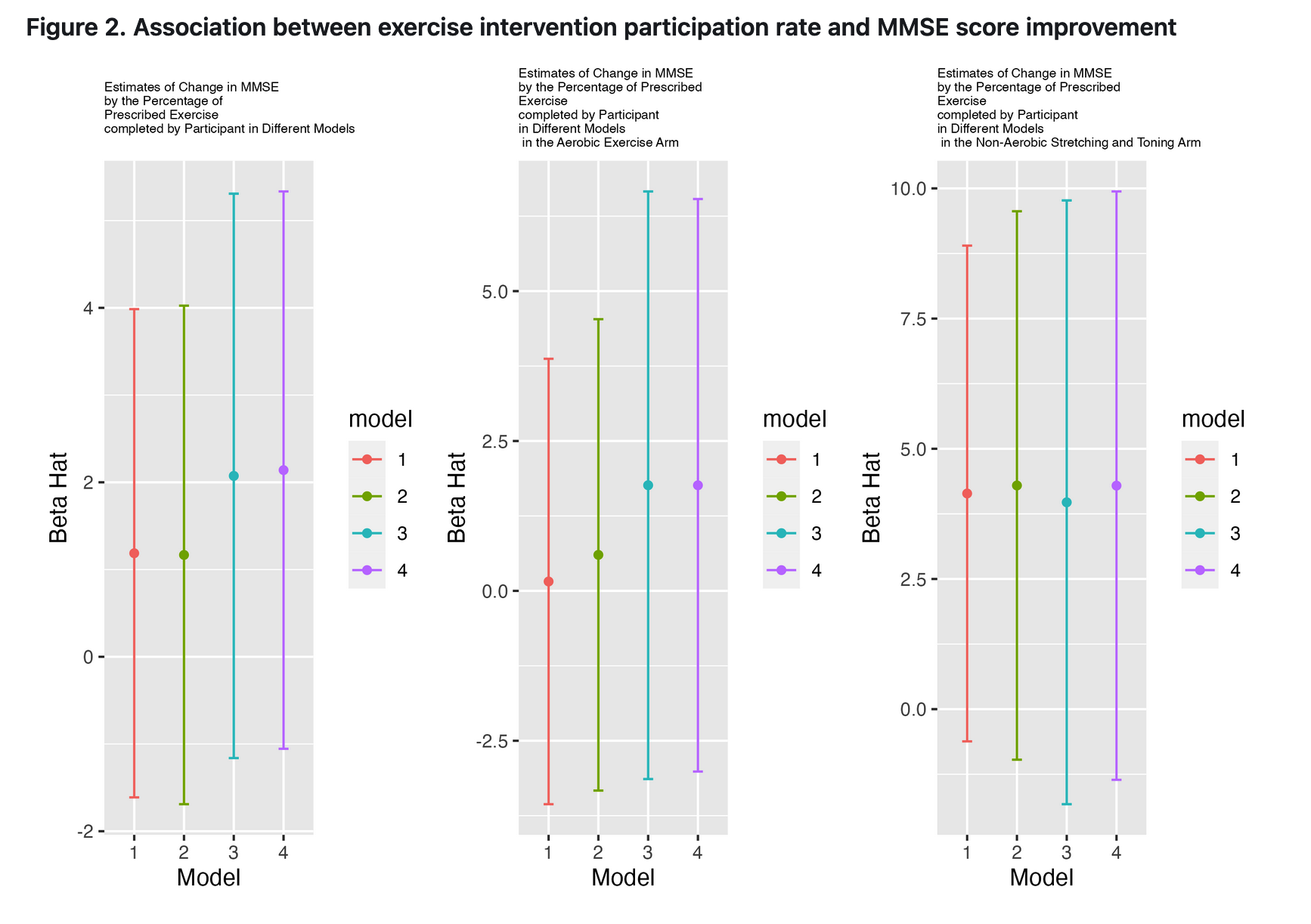
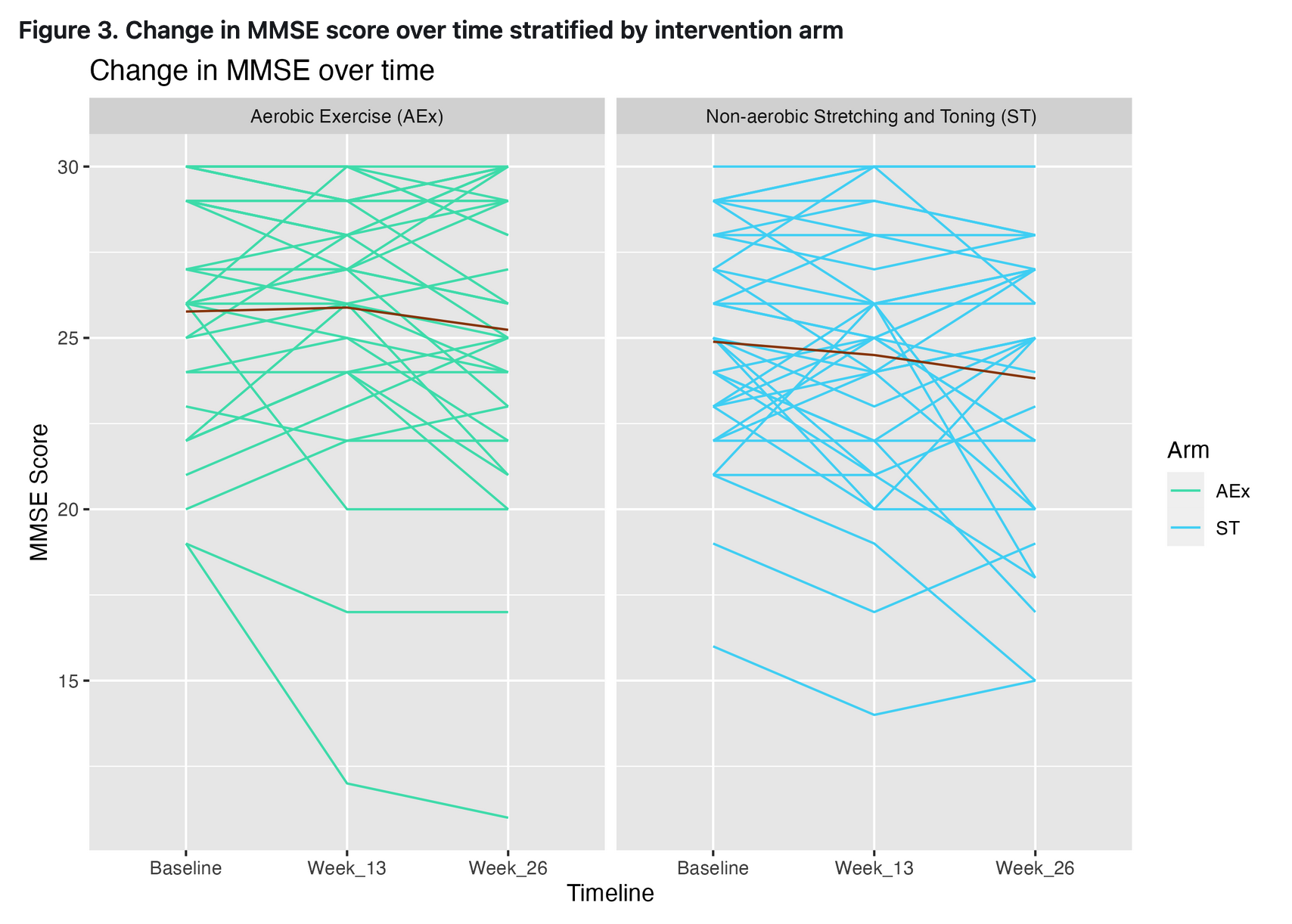
Conclusion
In conclusion, although there was no statistically significant changes in MMSE scores according to exercise intervention completion rates in either exercise arms, we believe meaningful trends were observed. There seems to be an improvement in MMSE scores after exercise interventions - especially from non-aerobic stretching and toning exercises. The statistical nonsignificance may be due to the relatively small sample size as well as the independent variable (exercise completion rate) that we used in the multivariate regression model, as it was in decimals rather than %.
from this …



… to this is amazing!


jarvis’ padawans
Introduction
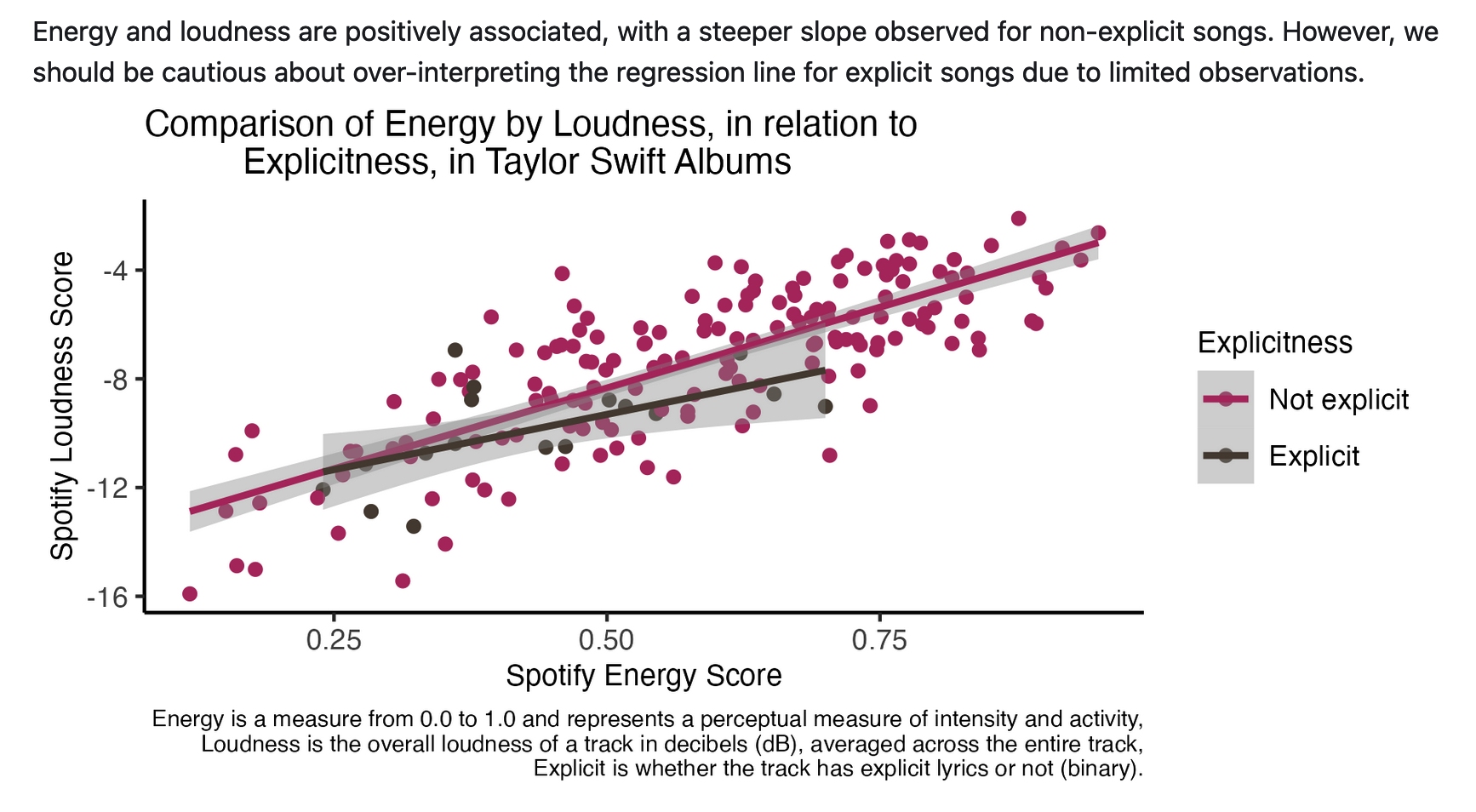
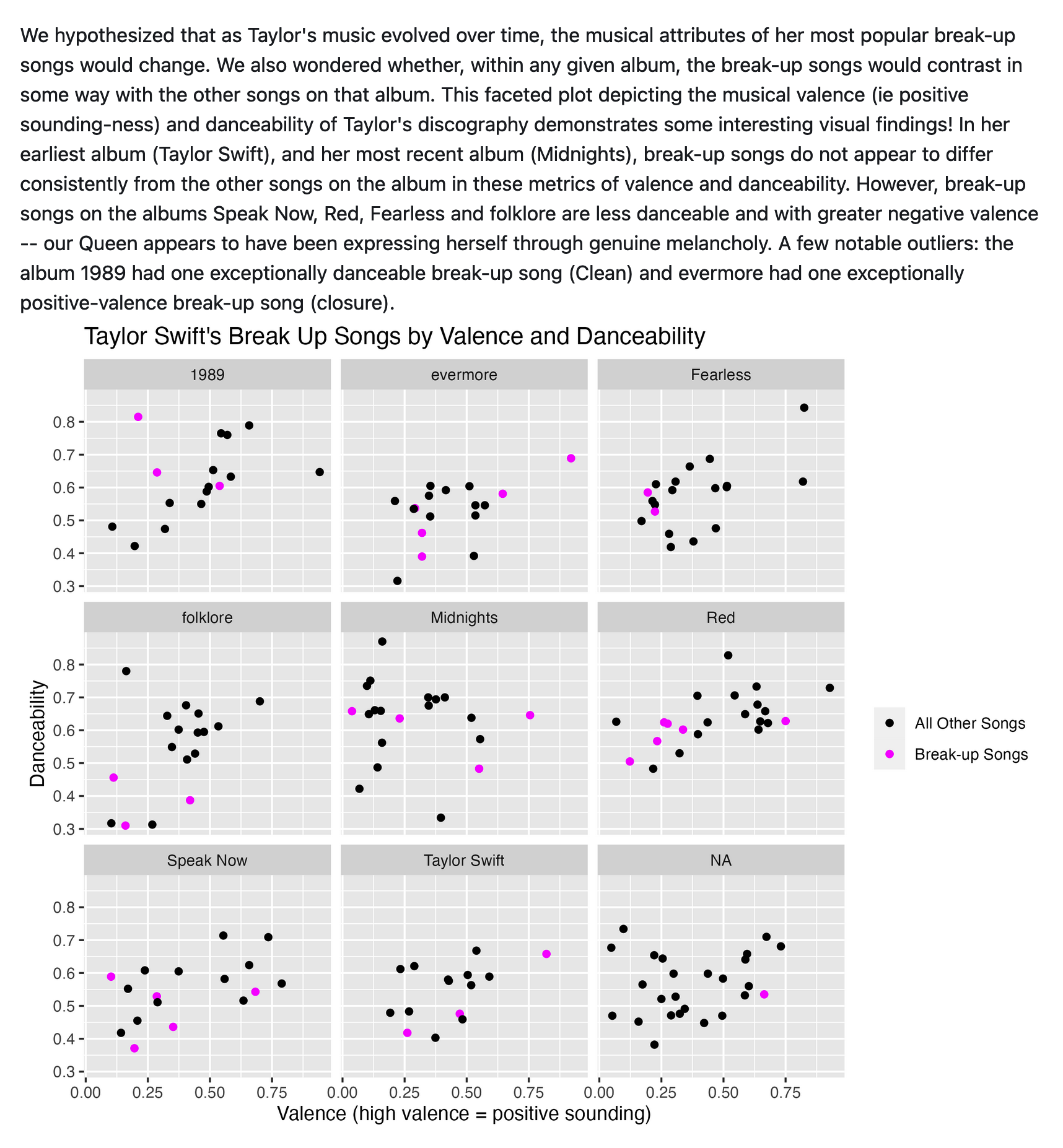
As one of the pre-eminent pop music stars of our very digital time, Taylor Swift and her music have far-reaching influence – culturally, socially, and even financially (as economic evaluations of her recent ERAS tour have demonstrated). As her popularity has increased, her music has evolved to include a range of genres and styles. However, several themes have been preserved throughout this evolution, including self-confidence, heartbreak, nostalgia.
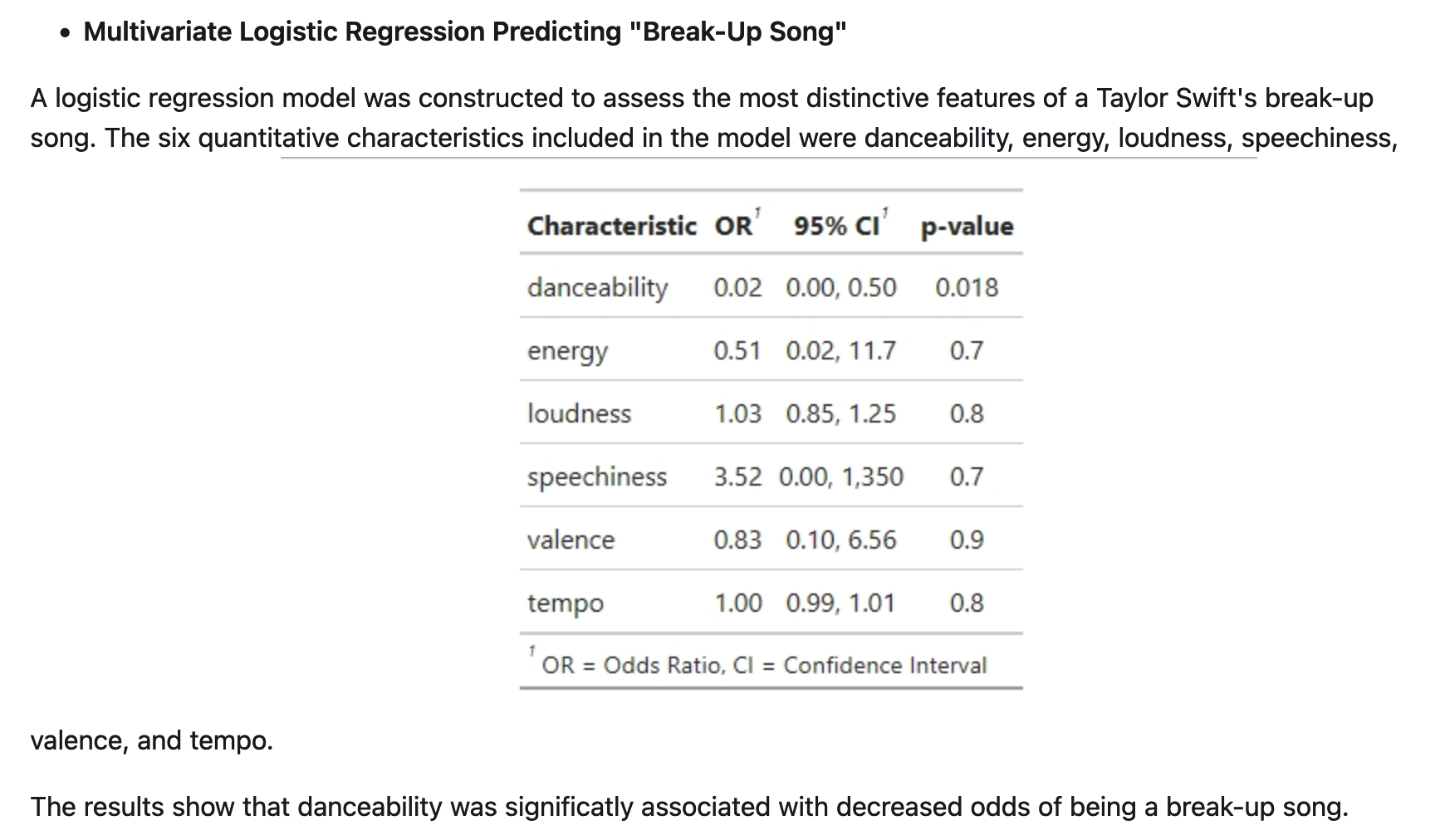
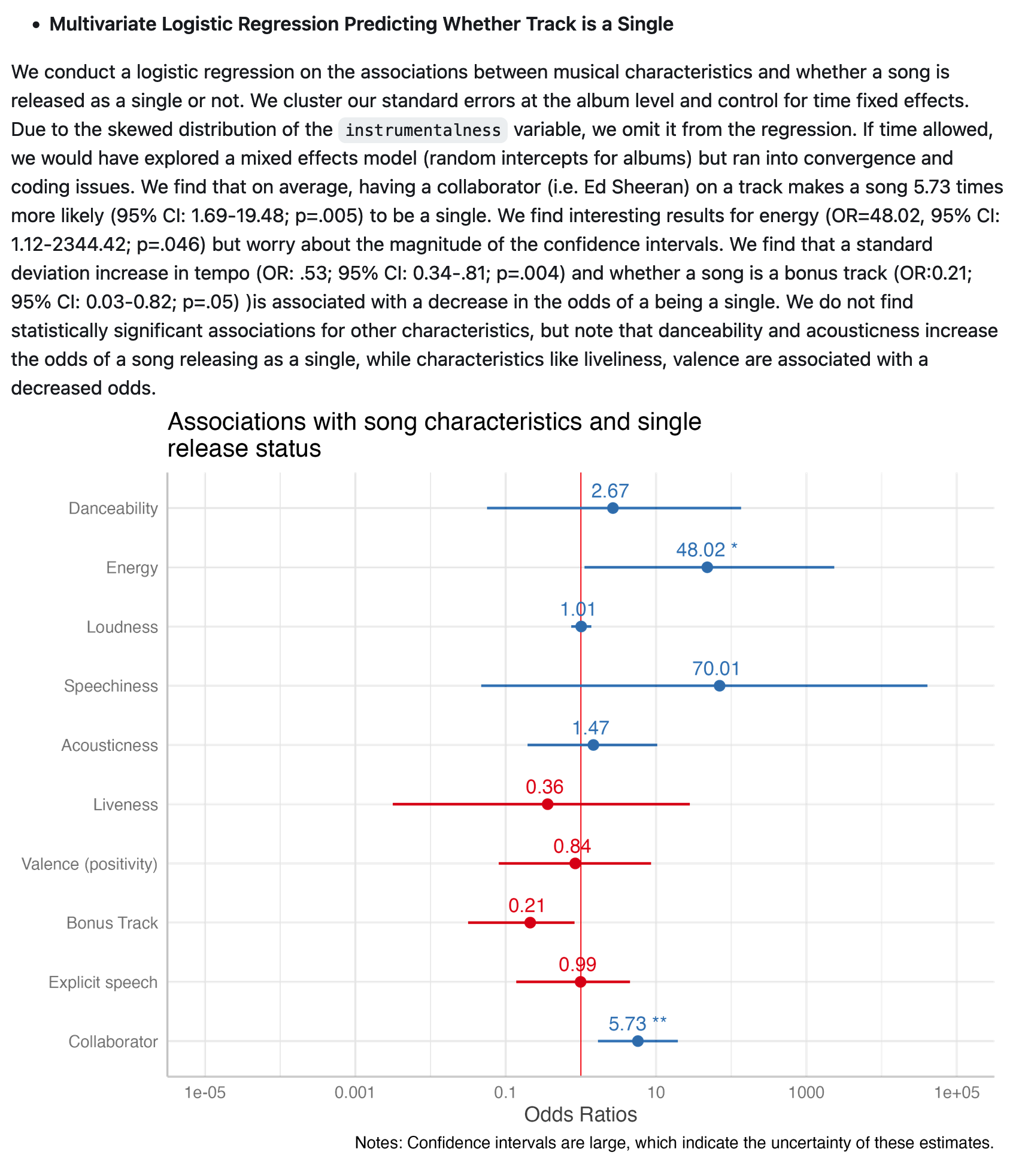
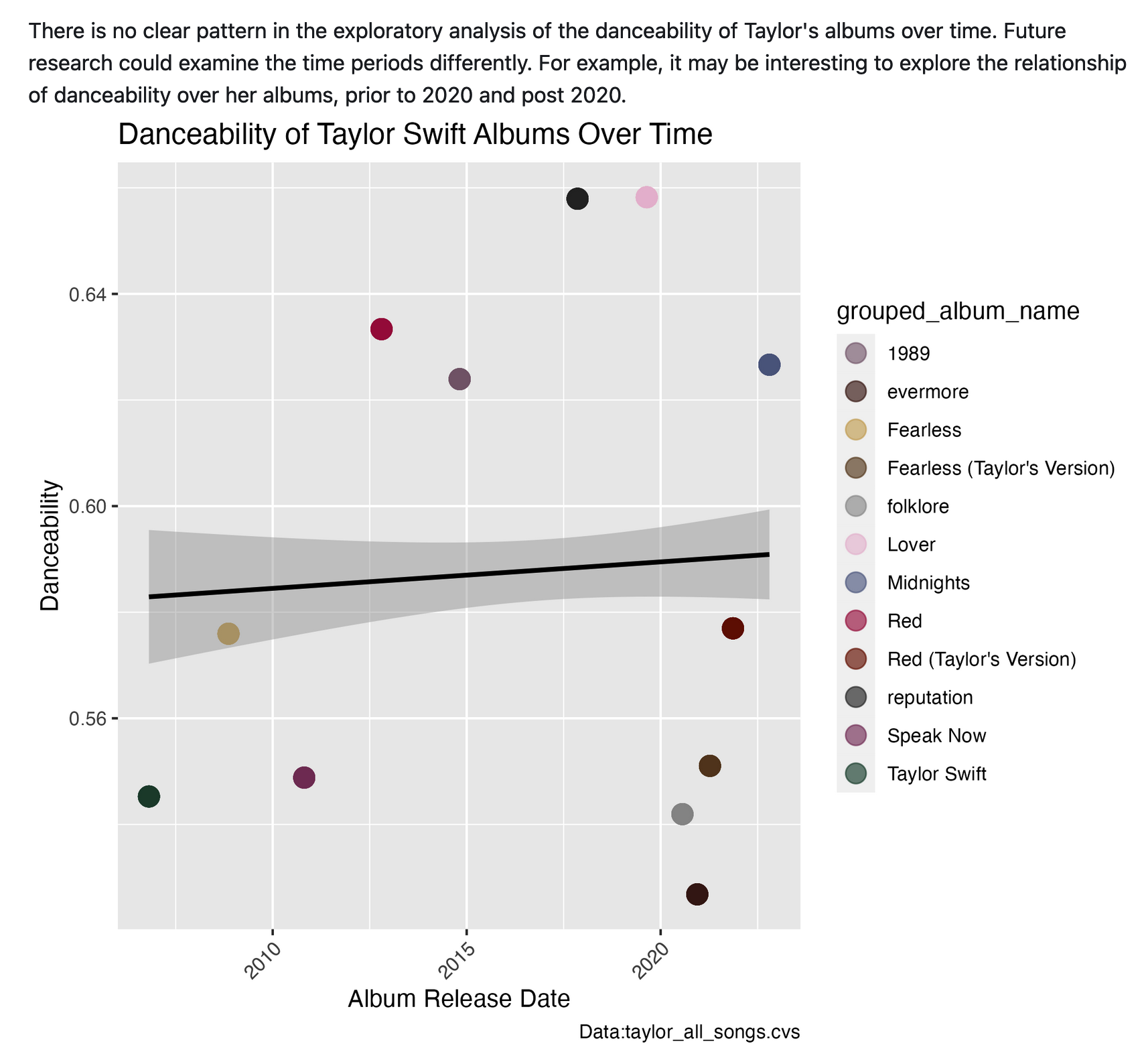
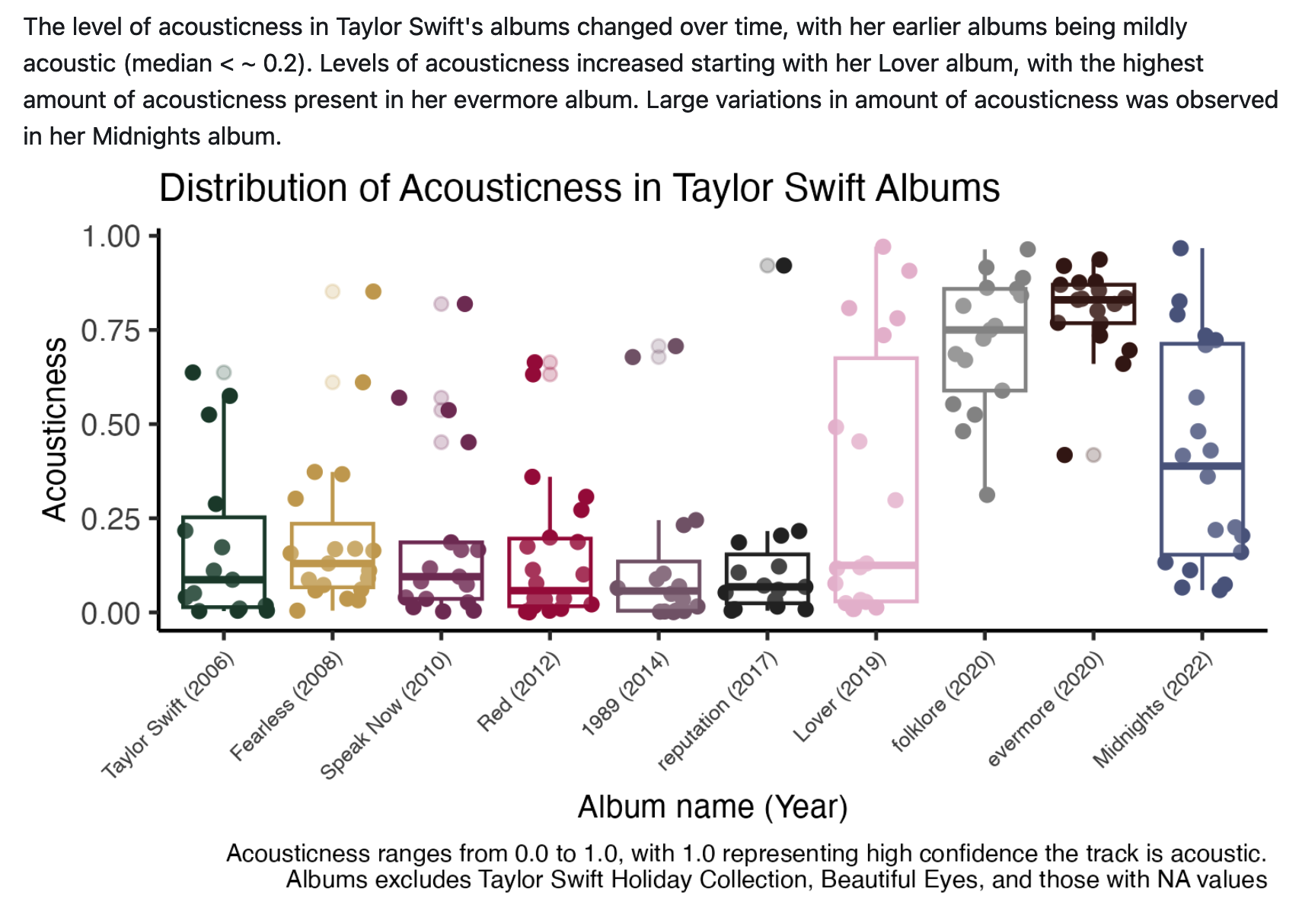
One of the most remarkable aspects of her music is its relatability, especially regarding commentary on relationships and break-ups. Vulture published an article ranking her break-up anthems – of which there are 44, spanning 10 of her 23 albums . Our analysis explores various patterns in emotion-related aspects of her music, including energy, danceability, use of explicit language, and expert categorization (by Vulture) as a break-up song.
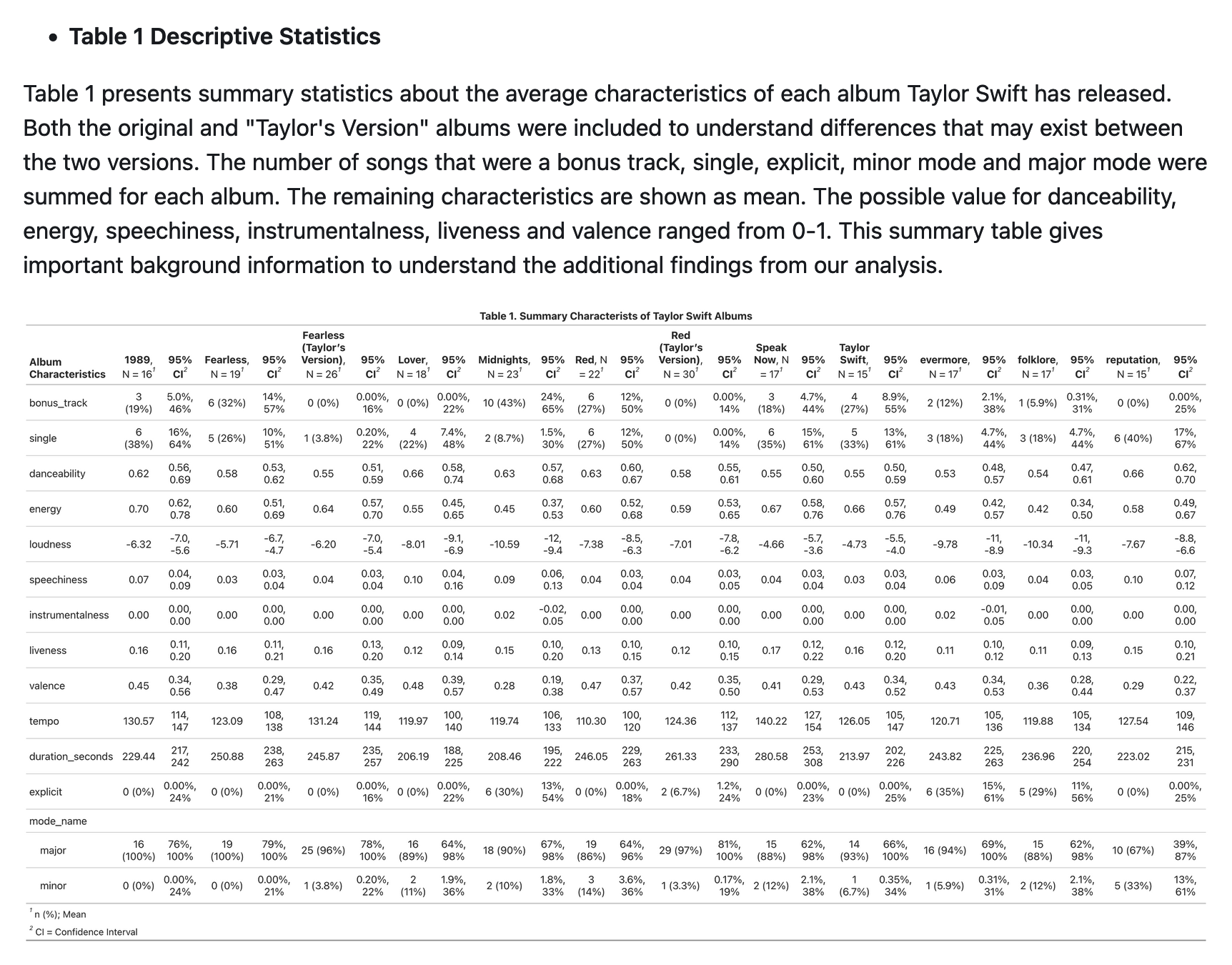
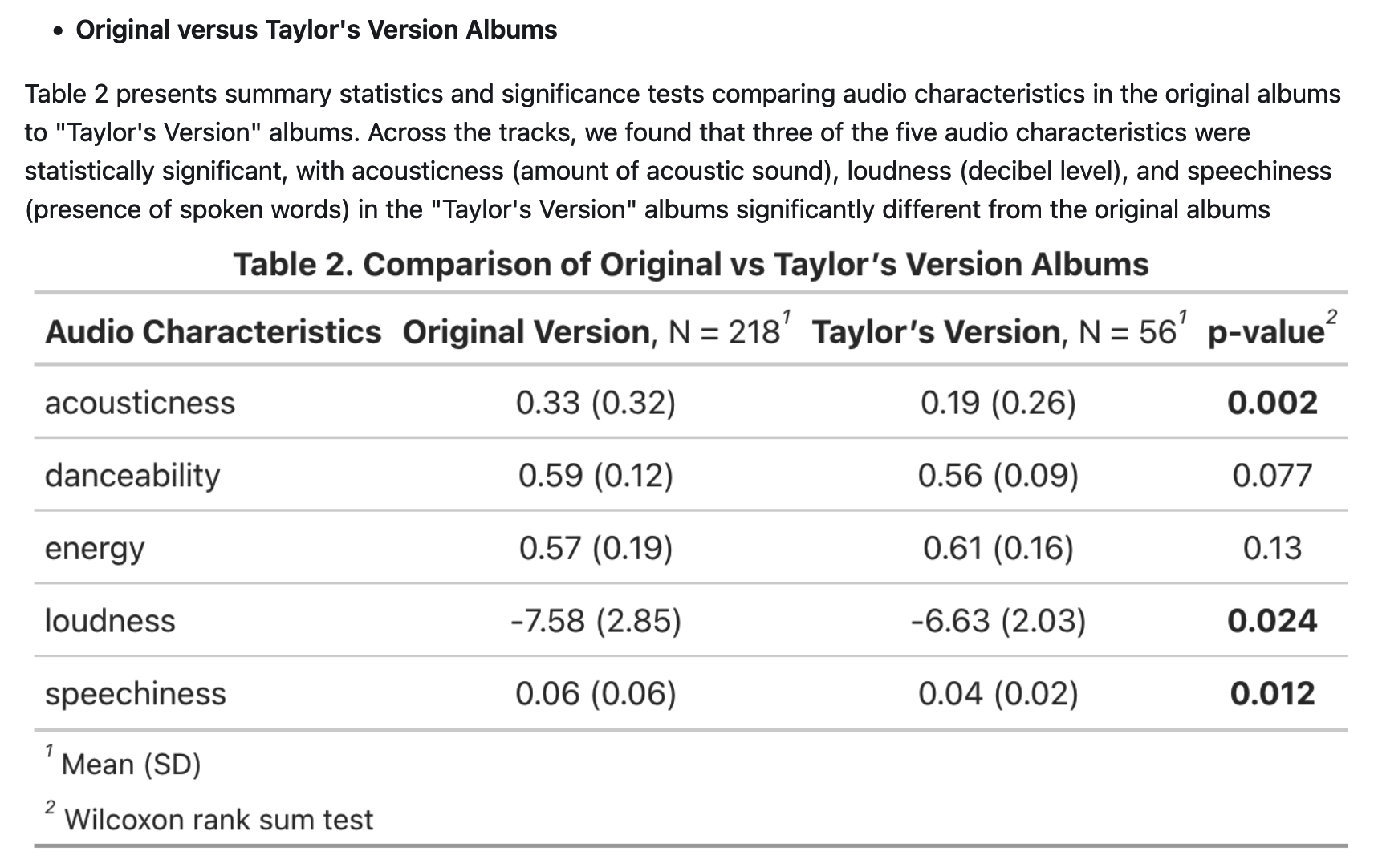
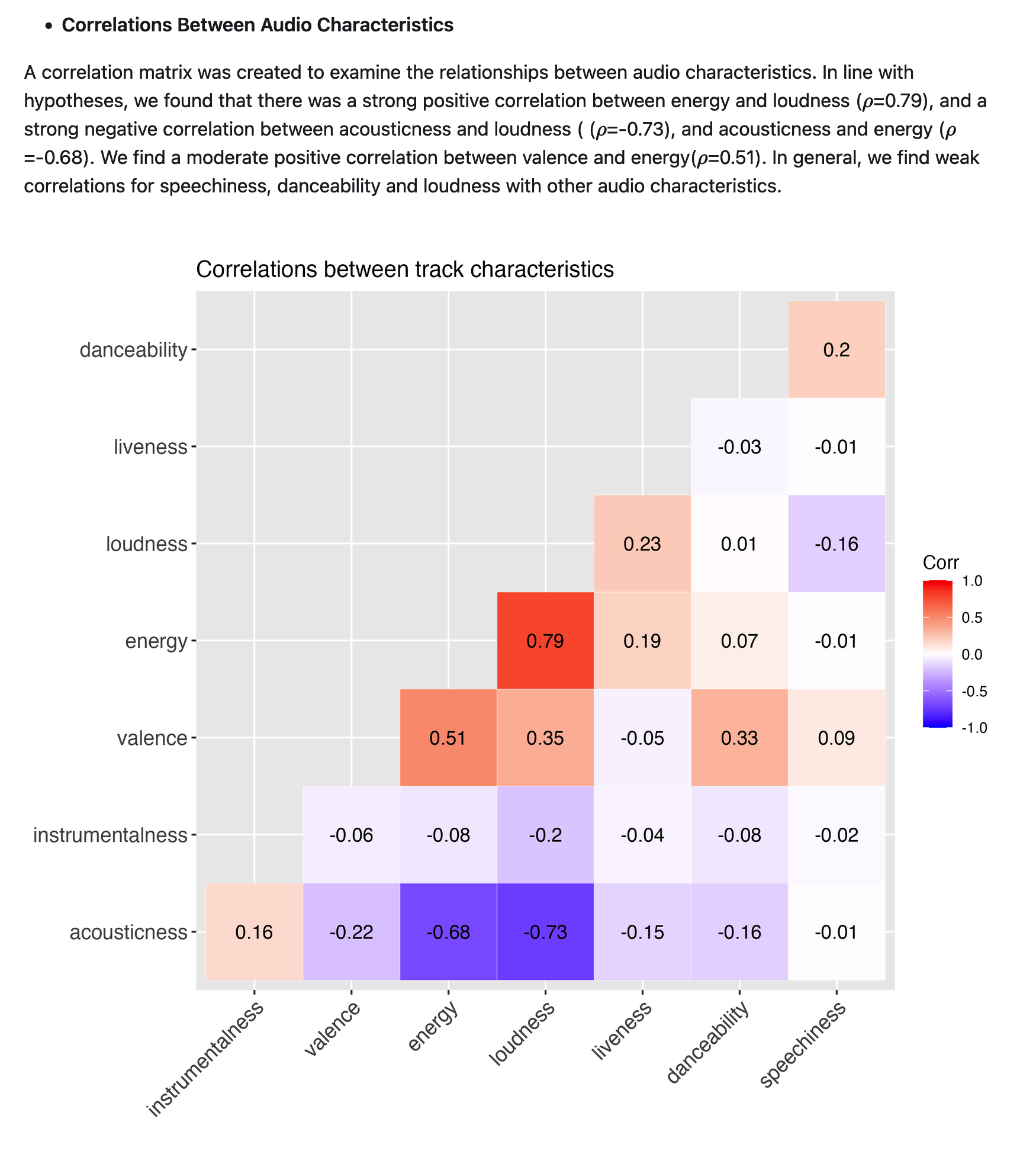

nice folder structure 👍

conclusions
Everyone did a great job!
- You all really impressed me!
- Several groups used the README.md file very well!
- Would loved to have seen use of README.Rmd with output_type: github_document
- Some people forgot to do author contributions
- Many very nice figures and tables were created
- You figured out quite elegant solutions to lots of coding challenges
- Many of you were able to successfully divide tasks and work well as a team!